Mini-Project for the course Optmization for Machine Learning (description here).
Topic:
- Meta-Learning/AutoML: Learning the learning rate.
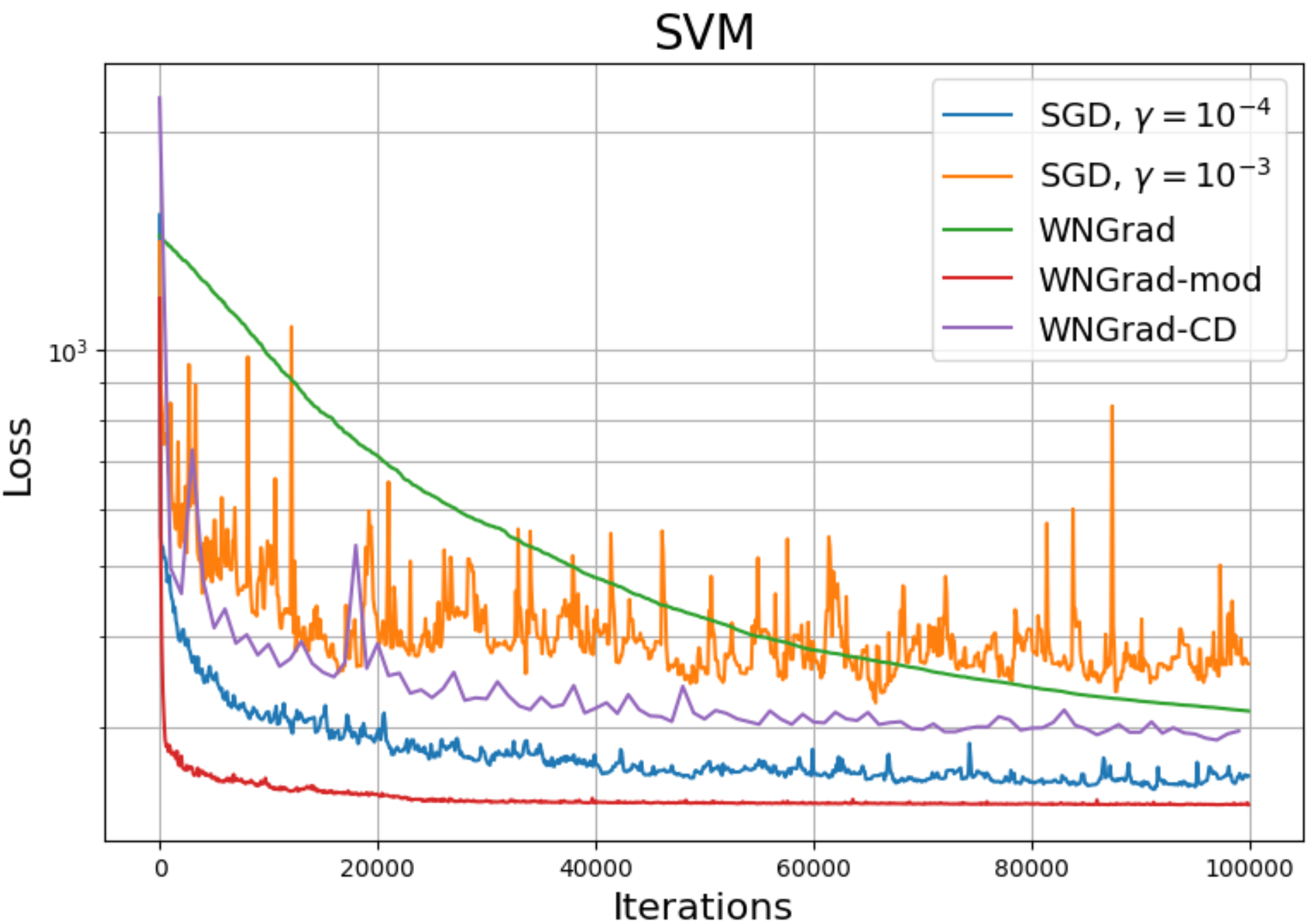
In this project we have implemented the algorithm WNGrad presented by Léon Bottou et. al. and compared its performance against other standard, gradient-based optimization algorithms. The main advantage of WNGrad over other algorithms like SGD or Adagrad is that, if there is a correct initialization, there is no hyperparameter to fine-tune -a process which can be very resource consuming-. We tried different problems, including convex problems (least squares, support vector machines) and non-convex problems (dense neural networks, convolutional neural networks).
Furthermore, after realizing that the parameter update proposed by Léon Bottou et. al. was too big and could truncate learning, we proposed a modification to the update rule, that proved to outperform WNGrad, and in some scenarios, a properly tuned SGD.
The convex and non-convex settings were performed in Python 3.9, using PyTorch 1.8.0 as core library. Experiments were performed on iPython notebooks.The Riemannian setting was performed in MatLab 2020b using, the manopt toolbox created and maintained by Boumal et al.
To reproduce the experiments performed in Python (Least Squares, SVM, and a CNN), run code/Main.ipynb. To reproduce the experiments in the Riemannian setting, run code/rayleighquotient/main.m and code/robustsubspaceanalysis/main.m.