A Python package for smoothing and refining geometries derived from raster data classifications. Smoothify transforms jagged polygons and lines resulting from raster-to-vector conversion into smooth, visually appealing features using an optimized implementation of Chaikin's corner-cutting algorithm.
Polygons and lines derived from classified raster data (e.g., ML model predictions, spectral indices, or remote sensing classifications) often have unnatural "stair-stepped" or "pixelated" edges that:
- Are visually unappealing in maps and GIS applications
- Can be difficult to work with in downstream vector processing
- Don't represent the real-world features they're meant to depict
Smoothify applies an optimized implementation of Chaikin's corner-cutting algorithm along with other geometric processing to create smooth, natural-looking features while:
- Preserving the general shape and area of polygons
- Supporting all shapley geometry types
- Handling shapes with interior holes
- Efficiently processing large datasets with multiprocessing
uv add smoothifyor
pip install smoothifyor
conda install conda-forge::smoothifyimport geopandas as gpd
from smoothify import smoothify
# Load your polygonized raster data
polygon_gdf = gpd.read_file("path/to/your/polygons.gpkg")
# Apply smoothing (segment_length auto-detected from geometry)
smoothed_gdf = smoothify(
geom=polygon_gdf,
smooth_iterations=3, # More iterations = smoother result
num_cores=4 # Use parallel processing for large datasets
)
# Or specify segment_length explicitly (generally recommended)
smoothed_gdf = smoothify(
geom=polygon_gdf,
segment_length=10.0, # Use the original raster resolution
smooth_iterations=3,
num_cores=4
)
# Save the result
smoothed_gdf.to_file("smoothed_polygons.gpkg")Example notebooks:
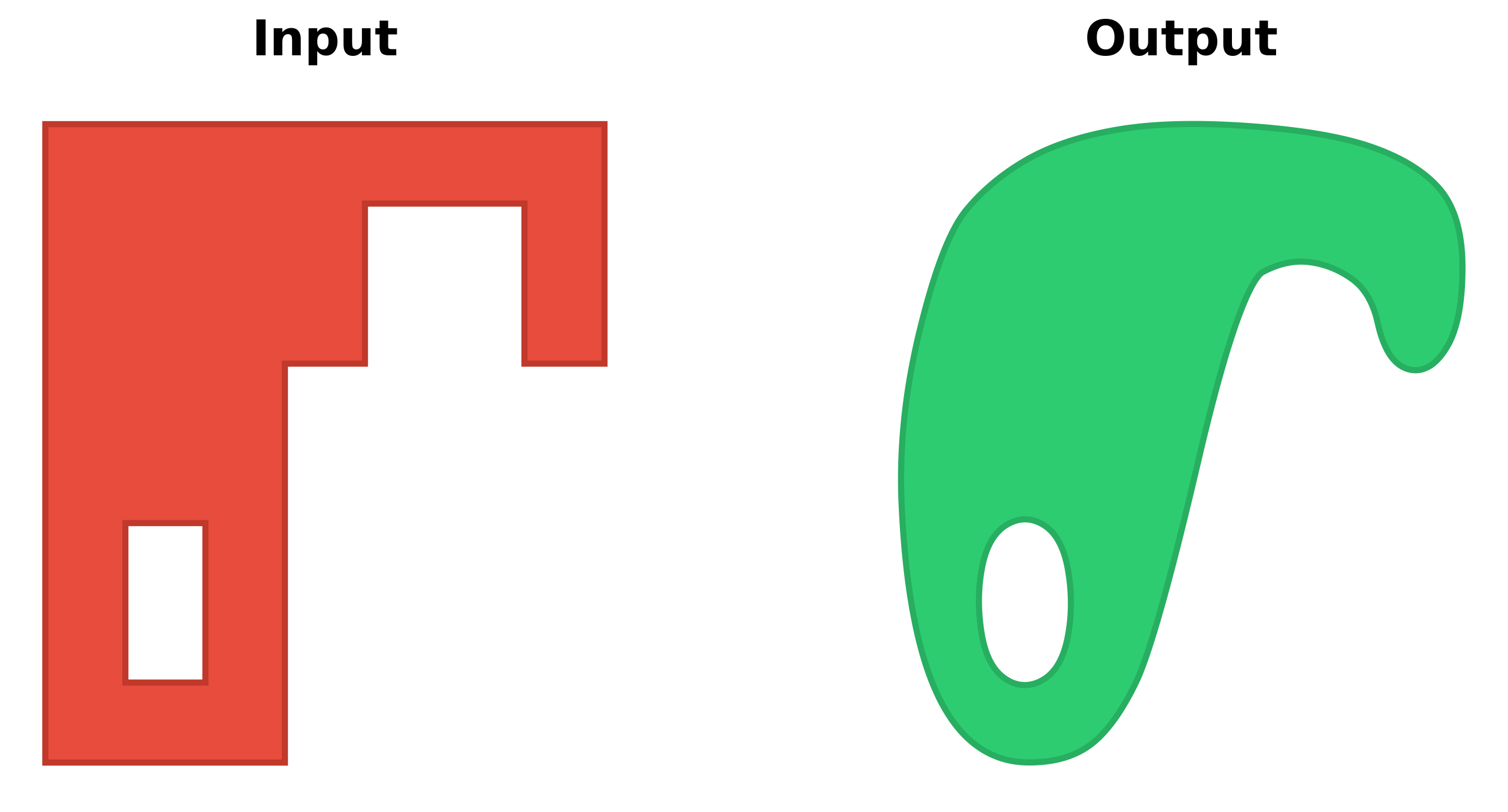
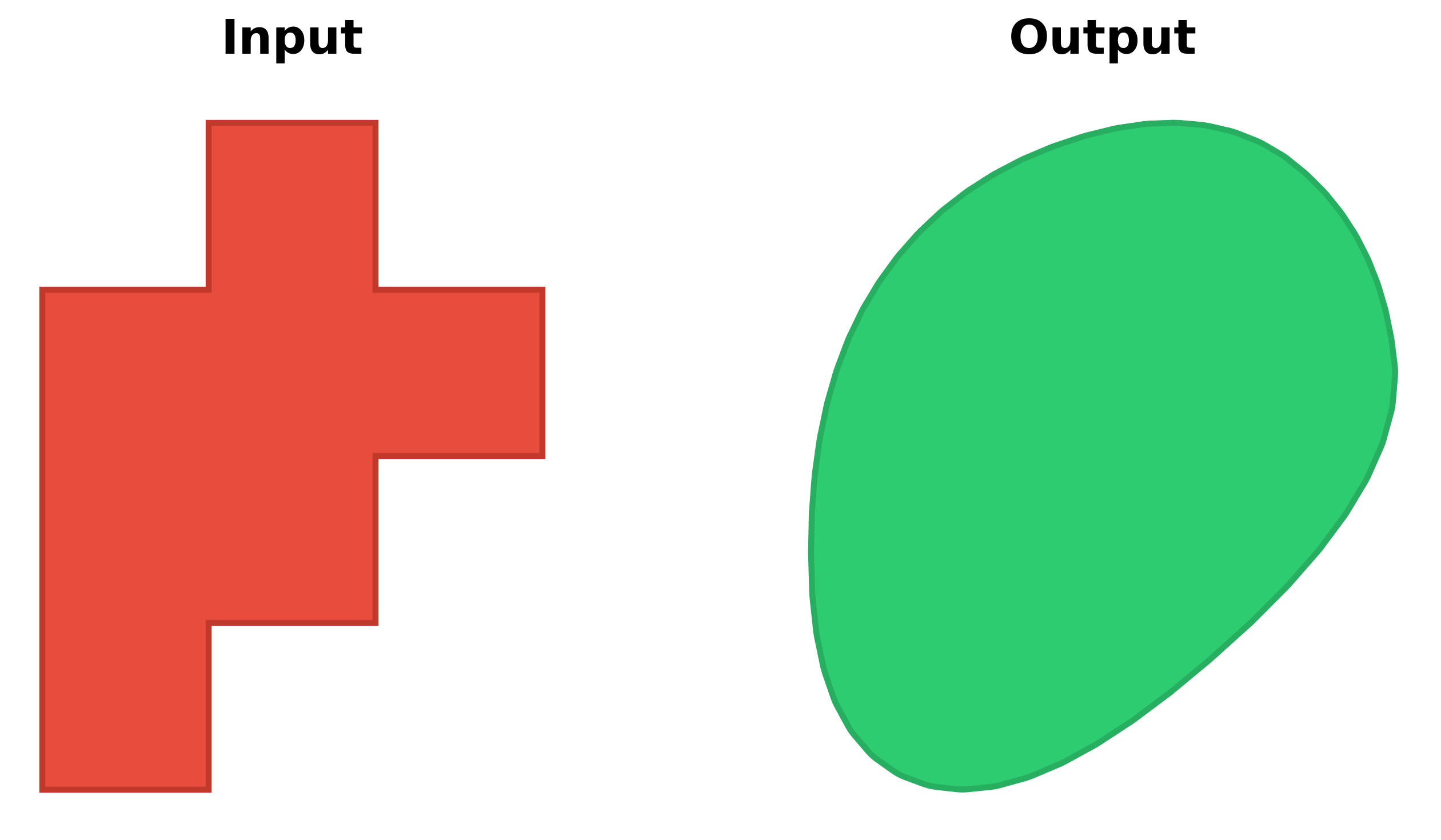
Transform pixelated polygons from raster data into smooth, natural-looking features:
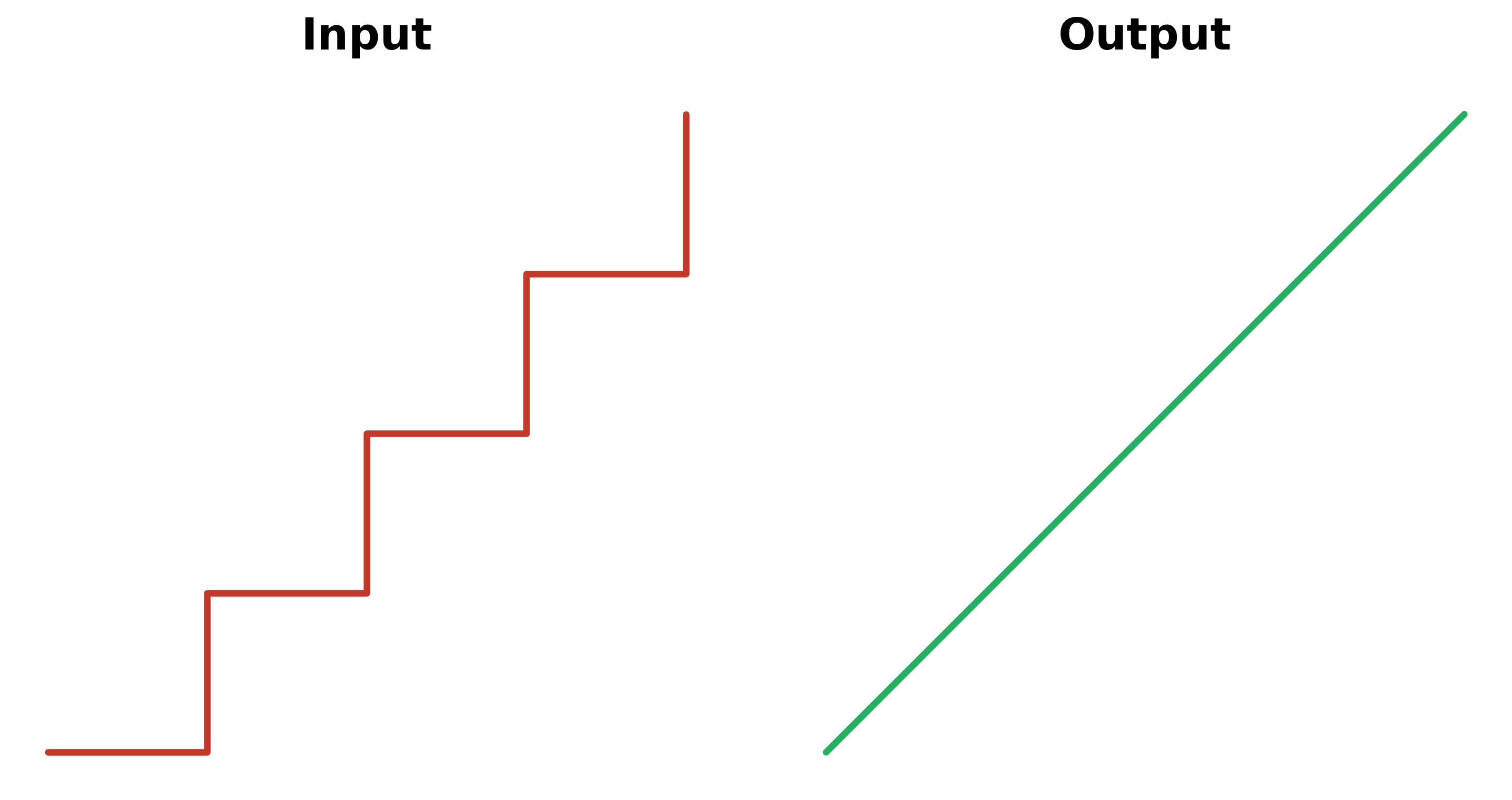
Works perfectly for roads, streams, and other linear features:
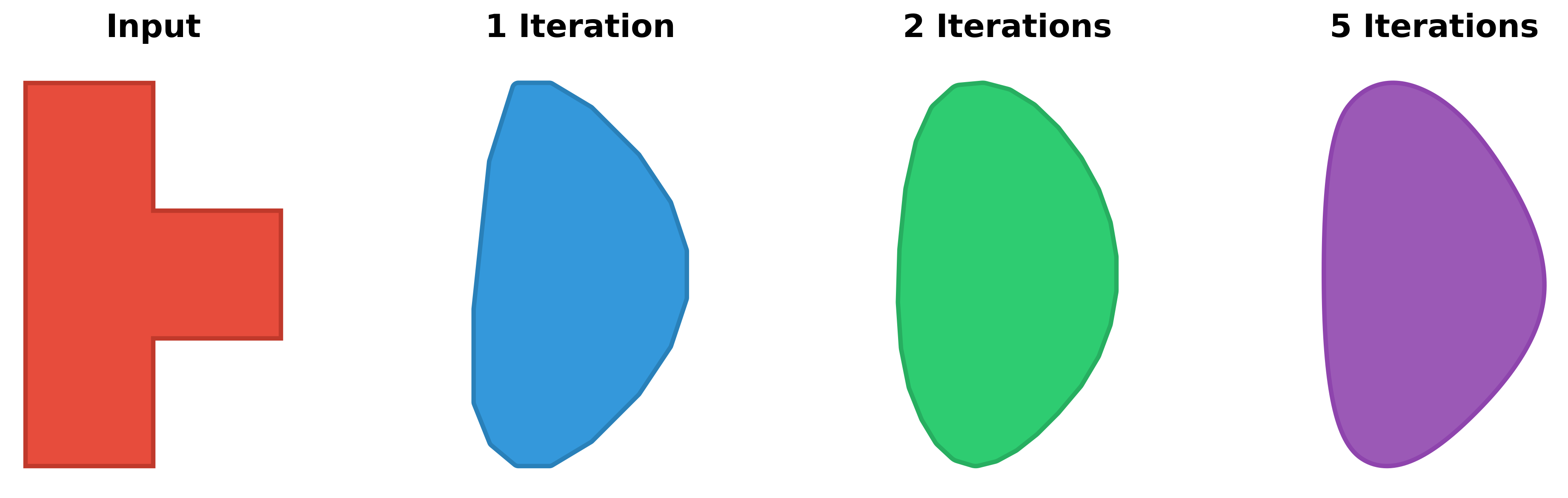
The smooth_iterations parameter controls how smooth the result will be:
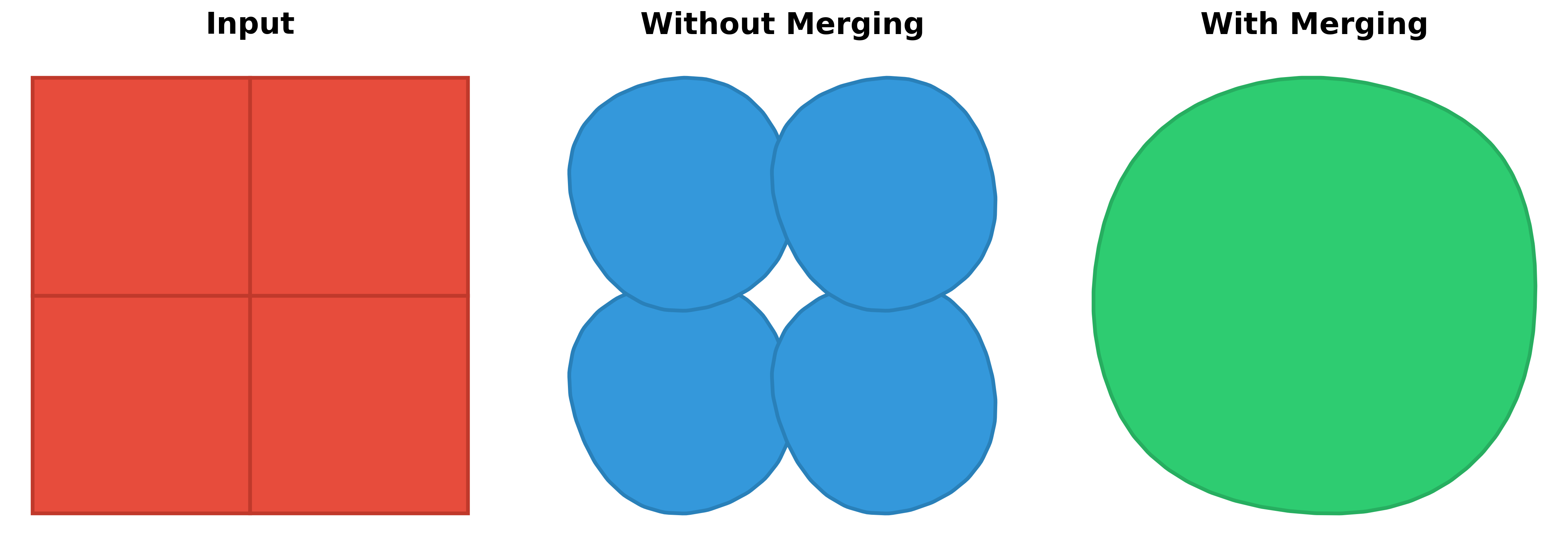
When processing multiple adjacent polygons, allowing merge_collection = True produces a combined result:
The smoothify() function accepts three types of input:
import geopandas as gpd
from smoothify import smoothify
# By default this will dissolve adjacent polygons before smoothing
gdf = gpd.read_file("polygons.gpkg")
smoothed_gdf = smoothify(
geom=gdf,
segment_length=10.0,
smooth_iterations=3,
num_cores=4
)
# Dissolve geometries by a specific field before smoothing
# Useful for merging adjacent polygons with the same classification
gdf_with_classes = gpd.read_file("classified_polygons.gpkg")
smoothed_by_class = smoothify(
geom=gdf_with_classes,
segment_length=10.0,
smooth_iterations=3,
merge_collection=True,
merge_field="land_type", # Merge adjacent geometries with same land_type
num_cores=4
)from shapely.geometry import Polygon
from smoothify import smoothify
polygon = Polygon([(0, 0), (10, 0), (10, 10), (0, 10)])
smoothed_polygon = smoothify(
geom=polygon,
smooth_iterations=3
)from shapely.geometry import Polygon, LineString
from smoothify import smoothify
geometries = [
Polygon([(0, 0), (10, 0), (10, 10), (0, 10)]),
LineString([(0, 0), (5, 5), (10, 0)])
]
smoothed = smoothify(
geom=geometries,
segment_length=1.0,
smooth_iterations=3
)| Parameter | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
geom |
GeoDataFrame, BaseGeometry, or list[BaseGeometry] | Required | The geometry/geometries to smooth |
segment_length |
float | None | Resolution of the original raster data in map units. If None (default), automatically detects by finding the minimum segment length (from a data sample). Recommended to specify explicitly when known |
smooth_iterations |
int | 3 | Number of Chaikin corner-cutting iterations (typically 3-5). Higher values = smoother output with more vertices |
num_cores |
int | 0 | Number of CPU cores for parallel processing (0 = all available cores, 1 = serial) |
merge_collection |
bool | True | Whether to merge/dissolve adjacent geometries in collections before smoothing |
merge_field |
str | None | GeoDataFrame only: Column name to use for dissolving geometries. Only valid when merge_collection=True. If None, dissolves all geometries together. If specified, dissolves geometries grouped by the column values |
merge_multipolygons |
bool | True | Whether to merge adjacent polygons within MultiPolygons before smoothing |
preserve_area |
bool | True | Whether to restore original area after smoothing via buffering (applies to Polygons only) |
area_tolerance |
float | 0.01 | Percentage of original area allowed as error (e.g., 0.01 = 0.01% error = 99.99% preservation). Only affects Polygons when preserve_area=True |
Smoothify uses an advanced multi-step smoothing pipeline:
- Adds intermediate vertices along line segments (segmentize)
- Generates multiple rotated variants (for Polygons) to avoid artifacts
- Simplifies each variant to remove noise
- Applies Chaikin corner cutting to smooth
- Merges all variants via union to eliminate start-point artifacts
- Applies final smoothing pass
- Optionally restores original area via buffering (for Polygons)
- Parallel Processing: For large GeoDataFrames or collections, use
num_cores= 0 to enable parallel processing - Smoothing Iterations: Values of 3-5 typically provide good results. Higher values create smoother output but increase processing time and vertex count
- Memory Usage: Scales with geometry complexity. The algorithm creates multiple variants during smoothing
- Optimal segment_length: Should match the original raster cell size (pixel size) or be slightly larger for best results
Contributions are welcome! Please feel free to submit a Pull Request.
- Fork the repository
- Create your feature branch (
git checkout -b feature/amazing-feature) - Commit your changes (
git commit -m 'Add some amazing feature') - Push to the branch (
git push origin feature/amazing-feature) - Open a Pull Request
This project is licensed under the MIT License - see the LICENSE file for details.