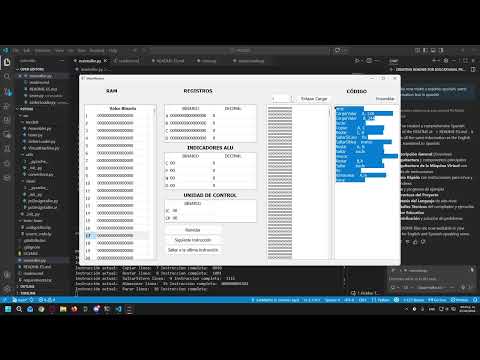
A Turing-complete educational PC simulator with integrated high-level language compiler, inspired by the "De Euclides a Java" textbook. This project demonstrates the complete compilation pipeline: from high-level language → lexical analysis → assembler → binary code → step-by-step instruction execution with real-time register visualization.
Developed for Universidad Nacional de Colombia
PCPENA (PC Simplified Simulator) is an interactive educational tool that allows students to:
- Write and compile high-level language programs
- Observe the lexical analysis and tokenization process using PLY (Python Lex-Yacc)
- See assembly code generation with label resolution and variable relocation
- Execute binary instructions on a virtual machine
- Visualize CPU state at each instruction: registers, RAM, ALU flags, and control unit
- Understand the complete compilation and execution cycle
High-Level Code → Lexer (PLY) → Parser → Assembler → Linker/Loader → Virtual Machine
- Uses PLY (Python Lex-Yacc) for tokenization
- Supports custom high-level language syntax
- Tokens include: numbers, operators, keywords, variables, functions, control structures
- Maintains symbol table for variable lookup
- Two-pass assembly compilation
- Pass 1: Labels resolution and variable allocation
- Pass 2: Opcode conversion to binary machine code
- Handles relocation of memory addresses
- Supports 14 instruction types
- Performs symbol resolution
- Loads binary code into virtual memory
- Relocates memory addresses based on program start point
- Initializes program counter and instruction pointers
- 4 General-Purpose Registers: A, B, C, D (16-bit each)
- 1024 Words of RAM (16-bit addressable cells)
- ALU Flags: Zero (C), Positive (P), Negative (N), Overflow (D)
- Control Unit: Manages instruction pointer and execution state
- PyQt5-based graphical interface
- Real-time visualization of: RAM, registers, ALU flags, control unit, object code
- Interactive buttons: Next, Last, Reset, Assemble, Link/Load
- Bridges machine model with PyQt5 view
- Updates GUI state after each machine operation
| Register | Code |
|---|---|
| A | 00 |
| B | 01 |
| C | 10 |
| D | 11 |
| Instruction | Opcode | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Parar | 0000000000000000 | Halt execution |
| Cargar | 0001 | Load from memory to register |
| CargarValor | 0010 | Load immediate value to register |
| Almacenar | 0011 | Store register to memory |
| SaltarSiCero | 010000 | Jump if zero flag set |
| SaltarSiNeg | 010001 | Jump if negative flag set |
| SaltarSiPos | 010010 | Jump if positive flag set |
| SaltarSiDes | 010011 | Jump if overflow flag set |
| Saltar | 010100 | Unconditional jump |
| Copiar | 011000000000 | Copy register to register |
| Sumar | 011000000001 | Add (result in first register) |
| Restar | 011000000010 | Subtract (result in first register) |
| Mult | 011000000011 | Multiply (result in first register) |
| Div | 011000000100 | Integer division (result in first) |
# Install system dependencies
sudo apt install python3-tk python3-dev
# Create virtual environment
python3 -m venv emuenv
source emuenv/bin/activate
# Install Python dependencies
pip install -r requirements.txt
# Run the simulator
python maintaller.py# Create virtual environment
python -m venv emuenv
emuenv\Scripts\activate
# Install Python dependencies
pip install -r requirements.txt
# Run the simulator
python maintaller.py- Write Assembly Code in the code editor
- Click "Ensamblar" to compile to binary
- Link and Load at desired memory address
- Execute Instructions step-by-step
- Monitor State: Registers, RAM, ALU flags, control unit
CargarValor A, 5 // Load 5 into register A
CargarValor B, 3 // Load 3 into register B
Sumar A, B // Add: A = A + B (8)
Almacenar A, 100 // Store to memory address 100
Parar // StopHere are some examples of the simulator in action:
Watch a complete demonstration of PCPENA in action:
This project teaches:
- Compiler Design: Lexical analysis, code generation
- Computer Architecture: Registers, memory, ALU operations
- Turing Completeness: Jump and arithmetic instructions
- Machine-Level Programming: Direct CPU interaction
Inspired by "De Euclides a Java" textbook - an educational resource on programming language design