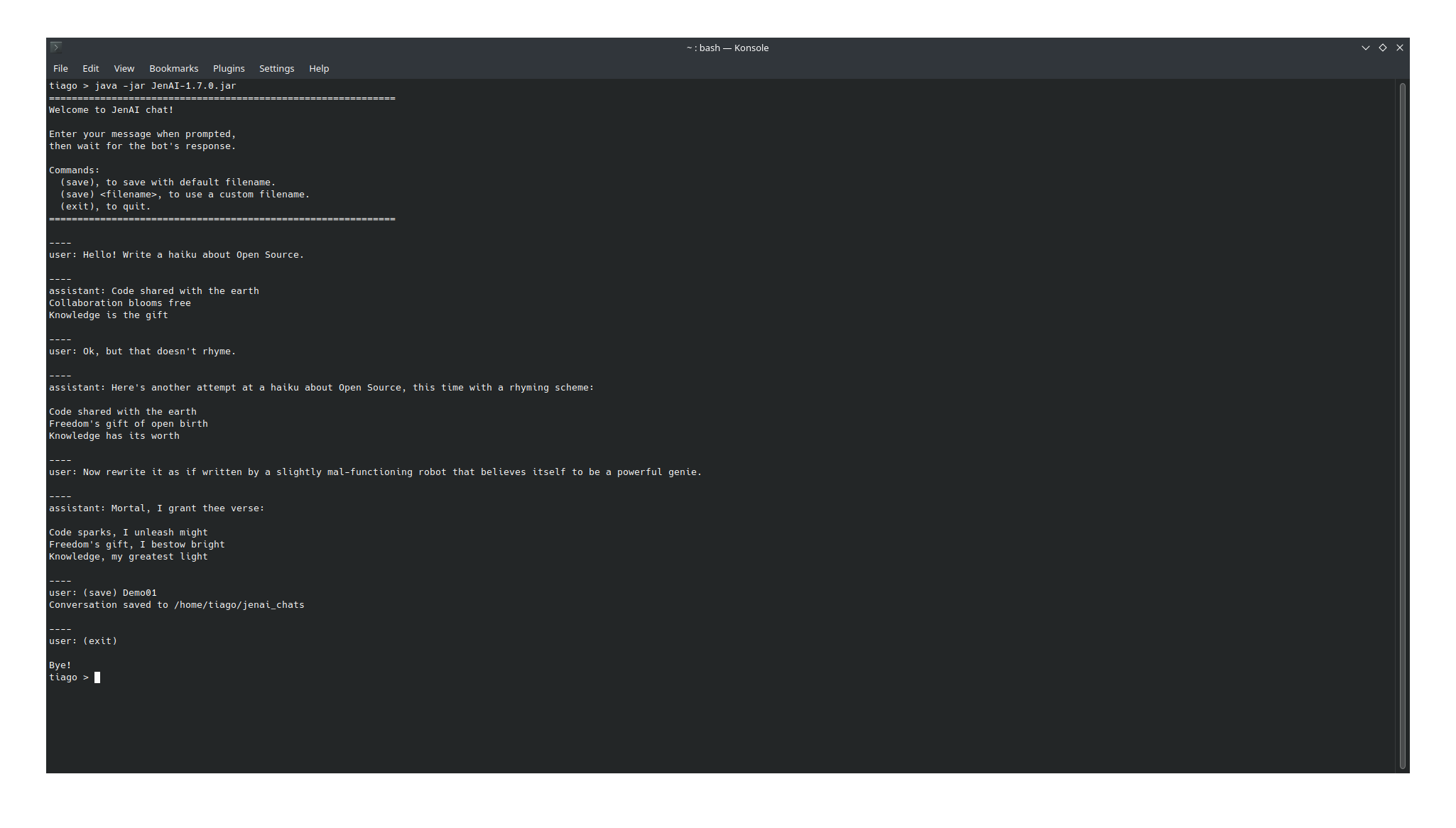
Simple CLI interface to chat with a local LLM.
Just type your message when prompted and press Enter to send it.
The application manages the conversation as a chat between the user (you) and the assistant (the LLM model), so any new message you send will be answered considering the context of the previous messages, up until the context size limit of the model being used. Once the limit is exceeded, the model will start losing the memory of the earliest messages in the conversation (it will probably still hallucinate answers about it if you ask).
You can save the conversation to disk by entering (save) as a message. This will create two files, one in plain text and one in json format, to a jenai_chats folder on the current working directory - if the folder does not exist, it will be created. When saving you can specify a custom filename to be used with (save) <filename>, otherwise the filename defaults to JenAI_chat_ with the date and hour as suffix.
To exit the conversation, simply type (exit) as your next message and send it.
The application assumes you have an LLM API listening on port 8080 of your computer (port number is configurable, check section below). If you have experience configuring and running them, any with an OpenAI-compatible API should work nicely - if you do not have experience, the easiest way to get one running is to use llamafile, which is both easy to use and has very good documentation on how to set it up.
Don't like the results you have been getting? Just try another model! Llamafile's documentation explains how to use a single executable to run different models, the same should be true for any other tool you might choose.
The application is written in Java, so you will need to have the Java runtime installed. Assuming it has already been installed, either download the Jar file from the latest entry in the Releases section of this repository or build the project following the instructions below, and execute it.
Example with llm server running on default port (8080):
$ java -jar JenAI.jar
Example using a custom port (8888, in this case):
$ java -jar JenAI.jar -p 8888
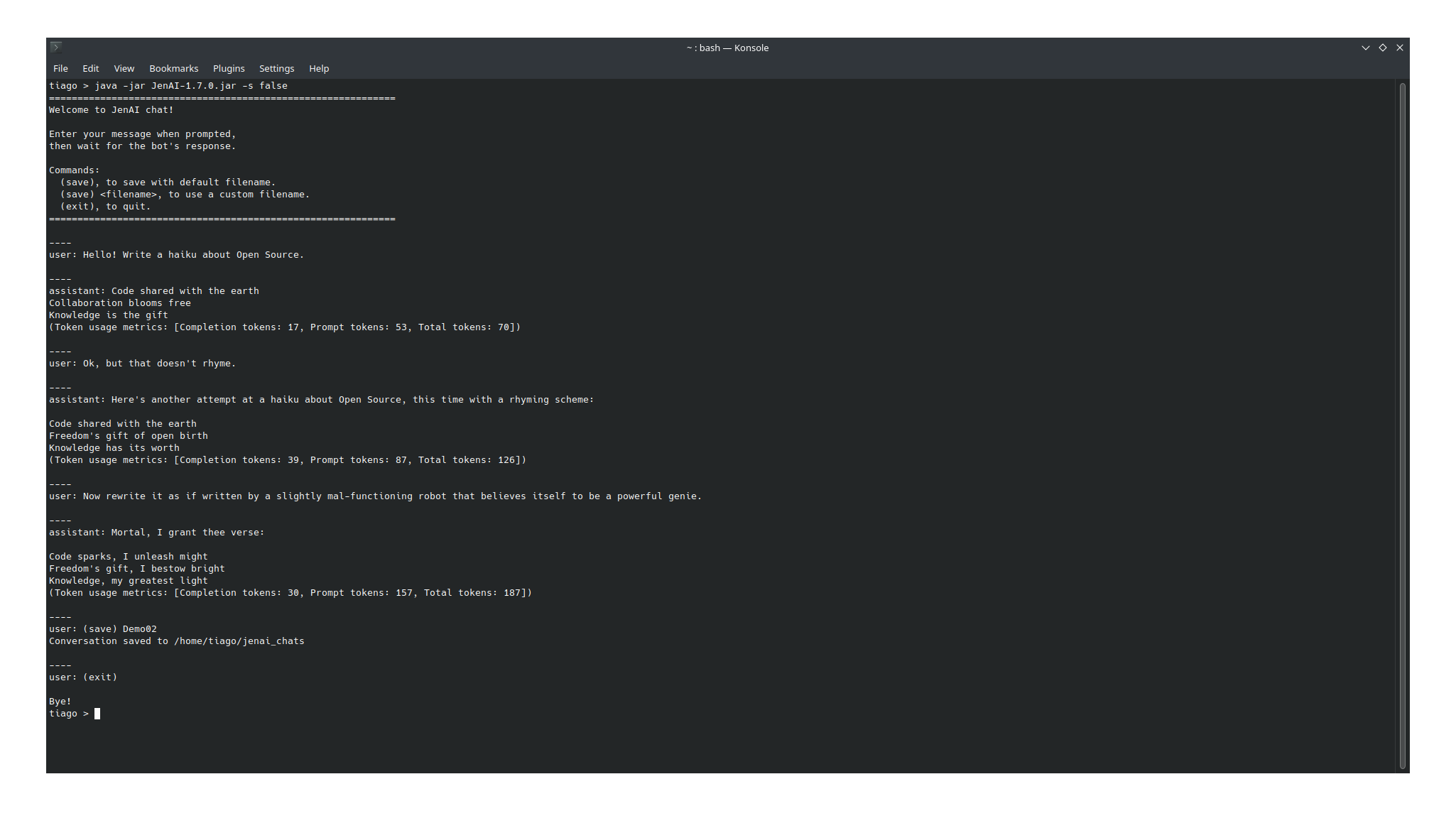
By default the application uses streaming response, with new tokens being displayed as soon as they are produced. This provides quick feedback and is useful when working with bigger models, that might take several minutes to produce the entire response. However, it is also possible to run it using block responses, displaying the response only when its entirety has been produced by the model - the advantage of this is that it allows for calculating the prompt usage metrics, which can help get a sense of when a model is likely to start forgetting earlier messages. Example using block responses (-s option stands for streaming, can be set to true or false):
$ java -jar JenAI.jar -s false
You can also start a conversation from a previously saved state (check How to use section for info about saving). For this, pass a -c option with the path from the current working directory to the json file that was saved (make sure to reference the JSON file, not the plain text one). Example:
$ java -jar JenAI.jar -c ./jenai_chats/JenAI_chat_2024-09-08_12-00-00_7167862348.json
If building the project with Maven, instead of JenAI.jar be sure to use the path to the generated jar, which will be in the target directory and have the version as a suffix.
If you are using ollama for the LLM server, you will have to at a minimum pass the name of the model you want to chat with when starting the application by using the -m <model_name> option. You will probably also want to use ollama's default port, 11434. Here is an example of how to chat with llama3.1 using ollama (check ollama's documentation for other model options):
$ java -jar JenAI.jar -p 11434 -m llama3.1
Here is the list of command-line options available when starting the application:
-
-p <port_number>: Set the port where to reach the server, <port_number> must be an integer indicating a port in your machine with a LLM server listening. Defaults to 8080. -
-m <model_name>: Specify the name of the model to be used, <model_name> must be a string. Necessary when using ollama as backend, has no effect when using llamafile. -
-c <path_to_conversation_json_file>: Specify a conversation file from which to load the conversation. A conversation file is a JSON file containing the history of a conversation, it can be created within the application itself with the(save)command. -
-s <true|false>: Specify if should run in streaming response mode or block response mode. Streaming response offers quicker feedback and a more familiar experience to those used to working with LLMs, but does not provide the metrics about token usage. Block response only returns any feedback after the model has finished producing the answer, but provides metrics about token usage. Deafults to true. -
-t <temperature>: Specify the temperature to be used when generating an answer, the larger the temperature the more randomness it includes. must be a decimal number, and usually fits in the [0.0-1.0) range. Make sure to use a dot (.) and not a comma to separate the parts of the number. Defaults to 0.0.
These options are independent of each other, and can be combined as desired and in any order. Examples of using some of them can be found in section "How to run" of readme.
This is a simple Maven project, so the easiest way to build it is running mvn clean package in the JenAI folder (assuming Maven is installed - if not, check its site and install from there). A jar file containing everything the application needs to run will be created at JenAI/target/JenAI-<VERSION>.jar.
The simplest way is to run mvn test on the main folder of the application.
To get a short intro to how the code is organized, you can check architecture.md.