A governance-first GitHub-centric framework for AI-assisted software engineering framework with enforced standards, pre-commit, CI, and explicit operational contracts.
This framework enforces security, documentation consistency, and quality through automated checks and explicit AI agent instructions.
- Overview
- How This Repository Works
- Governance: Security and Documentation
- Requirements / Dependencies
- High-Level Architecture
- Installation
- Usage Examples
- Configuration
- Troubleshooting
- Security Notes
This repository provides a structured foundation for AI-assisted development
projects. Unlike traditional templates, this framework treats
documentation as executable instructions for AI agents. All AI tools
(Cursor, ChatGPT, Copilot, etc.) are required to follow the standards
defined in docs/ai/CONTEXT.md, making documentation the authoritative
governance mechanism.
Governance through Documentation: In this framework, documentation serves dual purposes:
- ✅ Human-readable guidance for developers and operators
- ✅ Machine-readable instructions for AI agents
The documentation files (docs/ai/CONTEXT.md, docs/requirements.md) are not
suggestions—they are mandatory behavioral contracts that AI agents must
follow. This approach ensures consistency, security, and maintainability
across all AI-assisted development work.
This repository serves as both:
- A GitHub Template: Use it to create new repositories with the framework
- A Working Framework: Once created, it provides governance and quality enforcement
When you use this template, you get a complete framework with:
| Component | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| ✅ Governance Documentation | Included | Standards and requirements that AI agents must follow |
| ✅ Security Enforcement | Included | Strict .gitignore policies and pre-commit hooks |
| ✅ Quality Gates | Included | Automated formatting, linting, and safety checks |
| ✅ Consistent Standards | Included | Bash, Python, YAML, and JSON formatting rules |
| ✅ CI/CD Pipeline | Included | Automated testing and quality checks on every PR |
| ✅ Issue & PR Templates | Included | Structured templates for bug reports and features |
| ✅ Helper Scripts | Included | Pre-commit wrapper and secret detection |
Core Governance Files:
docs/ai/CONTEXT.md (Authoritative)
↓
├─→ Defines AI agent behavior standards
├─→ Referenced by: README.md, scripts, CI
└─→ Must be followed by all AI tools
docs/requirements.md (Project Contract)
↓
├─→ Defines project-specific requirements
├─→ Maps to acceptance criteria
└─→ Updated before implementation
README.md (User Documentation)
↓
├─→ Human-readable project overview
├─→ References CONTEXT.md standards
└─→ Provides usage examples
Quality Enforcement Chain:
Developer/AI Agent
↓
Makes changes
↓
Runs: ./scripts/run-precommit.sh
↓
Pre-commit hooks execute:
├─→ Formatting (Ruff, shfmt)
├─→ Linting (ShellCheck, PyMarkdown)
├─→ Secret detection (detect-secrets.sh)
└─→ Safety checks (private keys, merge conflicts)
↓
If passes → Commit succeeds
If fails → Commit blocked, review artifacts/pre-commit.log
↓
Push to GitHub
↓
CI runs same checks (cannot be bypassed)
↓
If CI passes → PR can be merged
AI agents working in this repository follow a strict workflow:
- Read Governance Documents First:
docs/ai/CONTEXT.mdanddocs/requirements.mdare authoritative - Respect Security Boundaries:
.gitignoreis strictly enforced—violations are security defects - Execute Quality Checks: Pre-commit must pass using
./scripts/run-precommit.sh - Update Documentation: Changes must be reflected in documentation
Governance is enforced through multiple layers:
| Layer | Mechanism | Purpose | Status |
|---|---|---|---|
| 📚 Documentation | docs/ai/CONTEXT.md, docs/requirements.md |
Defines mandatory AI behavior | ✅ Active |
| 🔍 Pre-commit | .pre-commit-config.yaml |
Catches issues before commit (formatting, linting, secrets) | ✅ Active |
| 🚀 CI/CD | .github/workflows/ci.yaml |
Enforces checks cannot be skipped, runs on all PRs | ✅ Active |
| 🔒 Security | .gitignore |
Prevents secrets and artifacts from being committed | ✅ Active |
Security is the highest priority in this framework. All contributors and AI agents must adhere to strict security standards.
⚠️ Critical Rule: Credentials, secrets, and sensitive configuration must never be committed to the repository.
How Secrets Are Handled:
-
Environment Files: All secrets must be stored in
.envfiles (or equivalent)- ❌
.envfiles are never committed (enforced by.gitignore) - ✅
.env.examplefiles must be committed to document required variables - ✅ Example files contain placeholder values, never real secrets
- ❌
-
What Is Protected: The
.gitignorefile protects:Category Protected Items Status 🔑 Environment Files .env,.env.*,vars.env✅ Protected 🔐 Credential Files .pem,.key,.crt,.pfx,.p12, SSH keys✅ Protected ☁️ Cloud Credentials .aws/,.gcp/,.azure/,terraform.tfvars✅ Protected 🚫 Generic Secrets secrets.*,*.secret,*.secrets✅ Protected -
AI Agent Requirements: AI agents must:
- Read
.gitignorebefore creating or modifying files - Never create, move, or commit ignored files
- Never log, echo, or persist secret values
- Use example files (e.g.,
.env.example) for documentation only - Treat violations of
.gitignorerules as security defects
- Read
-
Security Standards from CONTEXT.md:
- ❌ Never log secrets
- ❌ Credentials and IP addresses must never be hardcoded—use
.envfiles - ✅ Treat all inputs as untrusted
- ✅ Use least privilege
- ✅ Sanitize file paths and user input
- ✅ Document required permissions
| Enforcement Method | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 🔍 Pre-commit hooks | ✅ Active | Detect private keys and other secrets before commit |
| 🚀 CI workflows | ✅ Active | Run the same checks to prevent bypassing local checks |
📋 .gitignore is authoritative |
✅ Active | AI agents must respect it without exception |
Documentation in this repository serves as executable instructions for AI agents. This creates a governance model where:
- ✅ Documentation Defines Behavior:
docs/ai/CONTEXT.mdcontains mandatory standards that AI agents must follow - ✅ Requirements Are Contracts:
docs/requirements.mddefines the behavioral contract for the project - ✅ Consistency Is Enforced: All projects using this framework follow the same documentation structure
- ✅ AI Agents Are Accountable: AI agents cannot deviate from documented standards without explicit clarification
| File | Purpose | Audience | Status |
|---|---|---|---|
docs/ai/CONTEXT.md |
Mandatory AI behavior standards | AI agents (authoritative) | ✅ Required |
docs/requirements.md |
Project requirements and acceptance criteria | AI agents, developers | ✅ Required |
docs/ci-and-precommit.md |
Quality enforcement mechanisms | Developers, operators | ✅ Required |
docs/governance/ |
Project-specific governance documents | All stakeholders | |
README.md |
Project overview and usage | All stakeholders | ✅ Required |
Documentation Hierarchy:
-
docs/ai/CONTEXT.mdis authoritative for AI agents- Defines mandatory behavior standards
- Referenced by all other documentation
- Must be followed without exception
-
docs/requirements.mddefines the project contract- Maps requirements to acceptance criteria
- Must be updated before implementation
- Guides AI agent development work
-
README.mdprovides human-readable guidance- Explains how to use the framework
- Documents configuration and usage
- References CONTEXT.md for AI agent instructions
-
docs/governance/is for project-specific governance- Empty by default
- Add custom governance documents as needed
- Examples: coding standards, review processes, etc.
Per docs/ai/CONTEXT.md, all projects must include:
- ✅ README.md with: overview, tested-on shields, requirements/dependencies, architecture overview, installation, uninstall steps, usage examples, configuration, troubleshooting, security notes, license
- ✅ docs/runbook.md for operational tools
- ✅ Consistent formatting enforced by pre-commit (Markdown linting)
| Requirement | Version | Status |
|---|---|---|
| 🐧 Primary OS | RHEL 9 / RHEL 10 | ✅ Required |
| 🐧 Secondary OS | Ubuntu 22.04 | |
| 🐚 Shell | bash | ✅ Required |
| 🐍 Python | 3.11+ | ✅ Required |
- ✅
pre-commit(for quality checks) - ✅ Python packages as defined in
requirements.txtorrequirements-dev.txt(if present)
| Tool | Purpose | Status |
|---|---|---|
| 🐍 Ruff | Python linting and formatting | ✅ Active |
| 🐚 ShellCheck | Bash script linting | ✅ Active |
| 📝 shfmt | Bash script formatting | ✅ Active |
| 📄 PyMarkdown | Markdown validation | ✅ Active |
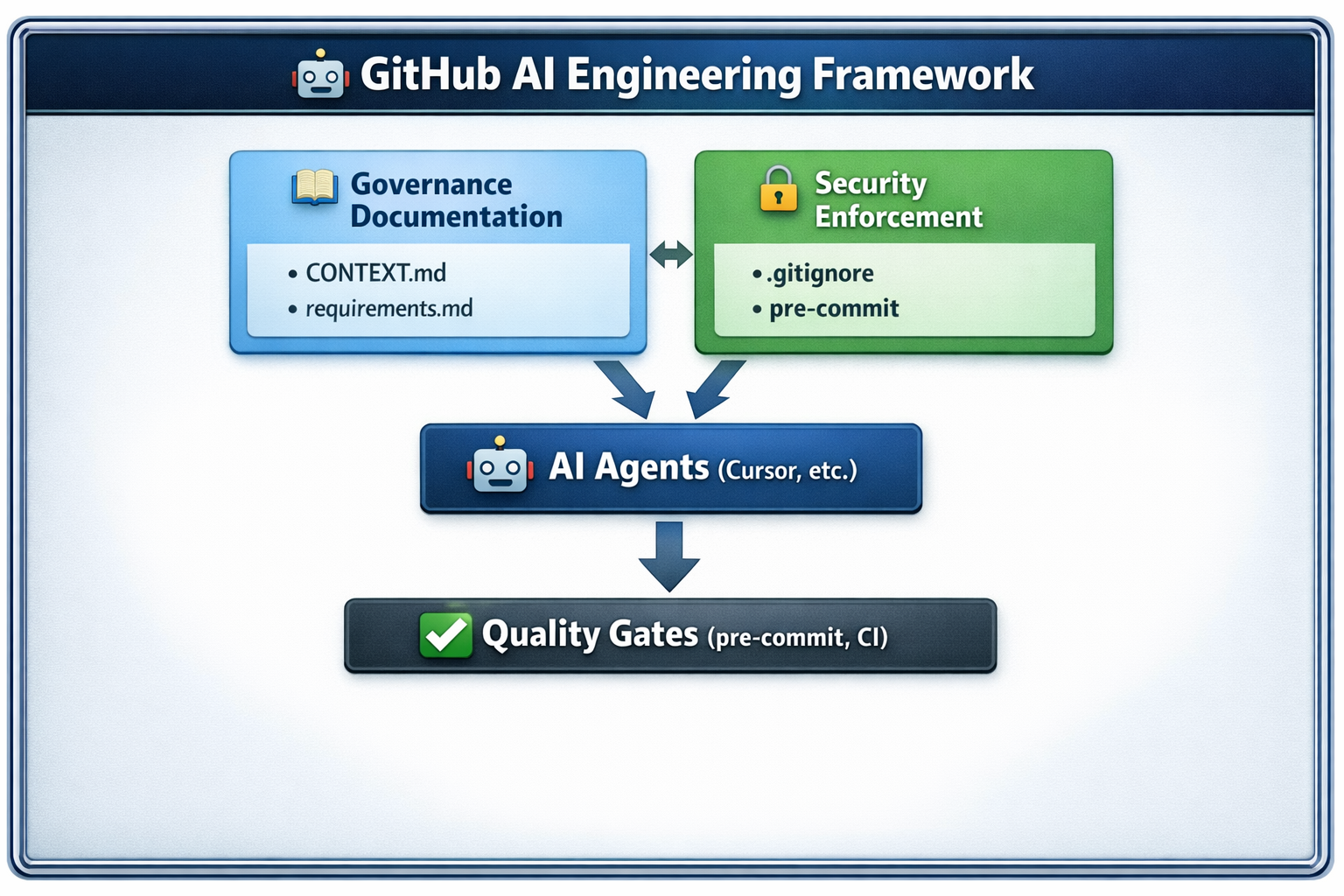
Key Components:
- 📚 Governance Layer: Documentation files that define mandatory behavior
- 🔒 Security Layer:
.gitignoreand pre-commit hooks that prevent secret leakage - 🤖 AI Agent Layer: AI tools that follow governance documentation
- ✅ Quality Gate Layer: Automated checks that enforce standards
This is a GitHub Template Repository. When you use it, GitHub creates a new repository with all the files from this template, giving you a complete framework for AI-assisted development with governance, security, and quality enforcement built-in.
Template Workflow:
- Create Repository: Use GitHub's "Use this template" button
- Clone & Setup: Clone your new repo and set up pre-commit
- Customize: Populate project-specific files and documentation
- Start Developing: Begin using the framework with AI agents
- Click "Use this template" on GitHub
- Choose a repository name and description
- Select public or private visibility
- Click "Create repository from template"
This creates a new repository with all framework files:
- ✅ Directory structure (
docs/,.github/,scripts/) - ✅ Configuration files (
.pre-commit-config.yaml,.gitignore, etc.) - ✅ Documentation templates (
CONTEXT.md,requirements.md) - ✅ CI/CD workflows (
.github/workflows/ci.yaml) - ✅ Helper scripts (
run-precommit.sh,detect-secrets.sh) - ✅ Issue and PR templates
git clone <your-new-repo-url>
cd <your-repo-name>pip install pre-commit
pre-commit installVerification Checklist:
- Pre-commit is installed
- Pre-commit hooks are installed
- Run
./scripts/run-precommit.shto verify setup
Required Customization:
-
docs/requirements.md: Define your project's requirements and acceptance criteria- Use the template structure provided
- Document functional and non-functional requirements
- Define acceptance criteria for each requirement
-
.env.example: Create an example environment file documenting required variables- List all environment variables your project needs
- Use placeholder values (e.g.,
YOUR_API_KEY_HERE) - Document what each variable is for
-
README.md: Update with your project-specific information- Replace framework description with your project description
- Update architecture diagram (if using image)
- Customize installation and usage sections
Optional Customization:
-
docs/governance/: Add project-specific governance documents -
docs/runbook.md: Create operational runbook (if applicable) - Issue Templates: Customize
.github/ISSUE_TEMPLATE/files if needed - PR Template: Customize
.github/pull_request_template.mdif needed
The bootstrap-template-structure.sh script recreates the template's directory
structure and empty placeholder files. Use it if:
- You accidentally deleted framework files
- You want to add the structure to an existing repository
- You need to restore the template structure
What It Creates:
Directories:
docs/,docs/ai/,docs/governance/.github/,.github/workflows/,.github/ISSUE_TEMPLATE/scripts/
Files (empty placeholders):
README.md,LICENSE,.gitignore.pre-commit-config.yaml,.pymarkdown.jsondocs/ai/CONTEXT.md,docs/requirements.md,docs/ci-and-precommit.md.github/workflows/ci.yaml.github/pull_request_template.md.github/ISSUE_TEMPLATE/feature_request.yml.github/ISSUE_TEMPLATE/bug_report.ymlscripts/run-precommit.sh,scripts/detect-secrets.sh
Usage:
./bootstrap-template-structure.shNote: The script will not overwrite existing files—it only creates missing files and directories.
To remove this framework's infrastructure from a project:
pre-commit uninstall-
.pre-commit-config.yaml -
.github/workflows/ci.yaml -
docs/ai/CONTEXT.md -
scripts/run-precommit.sh
pip uninstall pre-commit💡 Note: Consider keeping the governance documentation and quality checks even if removing other template components.
When instructing AI agents to work on this repository, always include:
Please follow the standards in docs/ai/CONTEXT.md and implement
the requirements in docs/requirements.md. Ensure pre-commit passes
before completing the work.The artifacts/ directory is automatically created and ignored by git. It
contains:
pre-commit.log: Detailed output from pre-commit runs- Created by
scripts/run-precommit.sh - Contains full hook output for debugging
- Useful for AI agents to review failures
- Uploaded as CI artifact on failure
- Created by
Note: The artifacts/ directory is in .gitignore and should never be
committed.
The framework includes structured issue templates:
Bug Reports (.github/ISSUE_TEMPLATE/bug_report.yml):
- Requires: Summary, reproduction steps, expected/actual behavior, environment
- Automatically labels issues as "bug"
Feature Requests (.github/ISSUE_TEMPLATE/feature_request.yml):
- Requires: Problem statement, desired outcome, acceptance criteria
- Automatically labels issues as "enhancement"
- Encourages requirement documentation before implementation
The PR template (.github/pull_request_template.md) ensures:
- ✅ Requirements coverage is documented
- ✅ Acceptance criteria are verified
- ✅ Security and safety checks are confirmed
- ✅ Testing evidence is provided
- ✅ Documentation is updated
This template enforces the discipline required by docs/ai/CONTEXT.md Section 10.
✅ Recommended method (for AI-assisted workflows):
./scripts/run-precommit.shWhat this script does:
- ✅ Runs all pre-commit hooks
- ✅ Captures output to
artifacts/pre-commit.logfor AI review - ✅ Preserves correct exit codes
Alternative method (automatic on commit):
git commit -m "Your message"
# Pre-commit runs automatically if installedStep-by-step checklist:
-
Copy the example file:
cp .env.example .env
-
Edit
.envwith your actual values (never commit this file) -
Verify
.envis in.gitignore(it should be automatically ignored)
Pre-commit hooks are configured in .pre-commit-config.yaml. The default configuration includes:
| Category | Tools | Status |
|---|---|---|
| 🔍 Basic checks | merge conflicts, YAML/JSON validation, trailing whitespace | ✅ Active |
| 🐍 Python | Ruff linting and formatting | ✅ Active |
| 🐚 Bash | ShellCheck and shfmt formatting | ✅ Active |
| 📄 Markdown | PyMarkdown validation | ✅ Active |
| 🔒 Security | Private key detection, API key detection, token scanning | ✅ Active |
The framework includes comprehensive secret detection via scripts/detect-secrets.sh:
What It Detects:
- ✅ API keys (Stripe, OpenAI, Google, AWS, etc.)
- ✅ GitHub tokens (PATs, OAuth tokens)
- ✅ Cloud provider credentials (AWS, GCP, Azure)
- ✅ Private keys (SSH, TLS, signing keys)
- ✅ OAuth tokens and refresh tokens
- ✅ JWT tokens
- ✅ High-entropy strings (potential secrets)
False Positive Filtering:
- ✅ Ignores variable names (e.g.,
api_key =) - ✅ Ignores example/placeholder values
- ✅ Ignores URLs and API endpoints
- ✅ Ignores comments and documentation
- ✅ Excludes test files and example files
If secrets are detected, the commit will be blocked. Use example placeholders like
YOUR_API_KEY_HERE instead of real secrets.
This framework includes two complementary CI workflows that run in parallel:
ci.yaml: Code quality and testing (pre-commit checks, unit tests)security-ci.yml: Security scanning (secret detection, SAST, dependency scanning)
The main CI workflow consists of two jobs that run sequentially:
Job 1: Pre-commit Checks (runs first):
- ✅ Runs on all pull requests and pushes to
main - ✅ Executes all pre-commit hooks (formatting, linting, secret detection)
- ✅ Uses Python 3.11 on Ubuntu latest
- ✅ If checks fail, generates detailed log via
scripts/run-precommit.sh - ✅ Uploads pre-commit log as artifact for review (only on failure)
Job 2: Unit Tests (runs after pre-commit passes):
- ✅ Only runs if pre-commit job succeeds
- ✅ Conditionally installs dependencies:
- Installs from
requirements.txtif present - Installs from
requirements-dev.txtif present - Installs
pytestonly iftests/directory exists
- Installs from
- ✅ Runs
pytestif tests exist, otherwise skips gracefully - ✅ Ensures code quality before running tests
Key Features:
- 🔒 Cannot be bypassed: All checks run in CI, preventing skipped local checks
- 📋 Artifact logging: Failed pre-commit runs generate downloadable logs
- ⚡ Efficient: Tests only run if pre-commit passes
- 🔄 Consistent: Same checks run locally and in CI
The security CI workflow runs in parallel with the main CI workflow and
provides comprehensive security scanning. This workflow is automatically
triggered on every pull request and push to main, and can also be run
manually via workflow_dispatch.
When It Runs:
- ✅ Automatically on every pull request (all branches)
- ✅ Automatically on every push to
mainbranch - ✅ Manually via GitHub Actions UI (
workflow_dispatch)
Job 1: Gitleaks Secret Scanning:
What It Scans:
- Full git history (including all commits, not just current changes)
- All file types in the repository
- Known secret patterns (API keys, tokens, credentials, private keys)
- High-entropy strings that may indicate secrets
How It Notifies:
- ❌ Fails the workflow if secrets are detected
- 📋 Detailed output in workflow logs showing:
- File path and line number where secret was found
- Secret type (e.g., "GitHub Token", "AWS Access Key")
- Commit hash where secret was introduced
- 🔴 Blocks PR merge until secrets are removed
Why It's Needed:
- Complements pre-commit
detect-secrets.sh(defense in depth) - Catches secrets that may have slipped through pre-commit
- Scans full git history (pre-commit only scans staged files)
- Provides comprehensive coverage of all repository content
Job 2: Semgrep SAST (Static Application Security Testing):
What It Scans:
- Security Audit Rules (
p/security-audit): Common security vulnerabilities - OWASP Top 10 (
p/owasp-top-ten): Top 10 most critical web application security risks - Code patterns that indicate security issues:
- SQL injection vulnerabilities
- Cross-site scripting (XSS) risks
- Insecure cryptographic usage
- Authentication and authorization flaws
- Insecure data handling
- And many more security anti-patterns
How It Notifies:
- 📊 GitHub Security Tab: Results uploaded as SARIF format
- Navigate to: Repository → Security → Code scanning alerts
- View detailed findings with code locations
- See severity levels and remediation guidance
- 📋 Workflow Logs: Detailed output in GitHub Actions logs
⚠️ Workflow Status: May fail if critical issues are found (configurable)- 🔔 GitHub Notifications: Security alerts appear in repository security dashboard
Why It's Needed:
- Detects security vulnerabilities in code patterns
- Identifies OWASP Top 10 risks before deployment
- Provides actionable remediation guidance
- Integrates with GitHub's security features
Job 3: OSV-Scanner Dependency Vulnerability Scanning:
What It Scans:
- Dependency files: Automatically detects and scans:
requirements.txt,requirements-dev.txt(Python)package.json,package-lock.json(Node.js)poetry.lock,Pipfile.lock(Python package managers)go.mod,go.sum(Go)Cargo.lock(Rust)Gemfile.lock(Ruby)- And many other dependency lock files
- Open Source Vulnerabilities (OSV) Database: Checks against known vulnerabilities in open source packages
- Transitive dependencies: Scans entire dependency tree, not just direct dependencies
How It Notifies:
- 📦 Workflow Artifact: JSON report uploaded as
osv-scan-results- Download from workflow run page
- Contains detailed vulnerability information
- Includes affected packages, severity, and remediation steps
- 📋 Workflow Logs: Summary output in GitHub Actions logs
⚠️ Workflow Status: Fails if critical vulnerabilities are found- 🔔 GitHub Dependabot Integration: Results complement Dependabot alerts
Why It's Needed:
- Identifies known vulnerabilities in dependencies
- Prevents vulnerable packages from being deployed
- Provides early warning of security issues in third-party code
- Complements GitHub's native dependency scanning
Key Features:
- 🔒 Defense in Depth: Multiple layers of security scanning
- 📊 GitHub Integration: SARIF results appear in Security tab
- ⚡ Parallel Execution: Runs simultaneously with main CI (faster)
- 🔍 Comprehensive: Covers secrets, code vulnerabilities, and dependencies
- 🚫 Non-Bypassable: Runs automatically on all PRs and pushes
- 📈 Actionable Results: Detailed findings with remediation guidance
Workflow Status and PR Requirements:
- Both
CIandSecurity CIworkflows must pass for PRs to be mergeable - Security failures block PR merge until issues are resolved
- Workflow status appears in PR checks section
- Detailed logs available in GitHub Actions tab
Viewing Results:
- Workflow Logs: GitHub Actions → Workflows → Security CI → View run
- Security Tab: Repository → Security → Code scanning alerts (Semgrep)
- Artifacts: Workflow run page → Artifacts (OSV-Scanner results)
- PR Checks: PR page shows workflow status and links to details
Note: See docs/security-ci-review.md for detailed integration guidance and
best practices.
Markdown linting rules are configured in .pymarkdown.json:
| Rule | Setting | Status |
|---|---|---|
| Line length | 120 characters | ✅ Active |
| Headers | First line doesn't need to be a header (md041 disabled) | ✅ Active |
| Blank lines | Required around lists and headers | ✅ Active |
| Inline HTML | Allowed (for image sizing) | ✅ Active |
Troubleshooting checklist:
- Review the log: Check
artifacts/pre-commit.logfor detailed error messages - Auto-fix issues: Many hooks auto-fix issues—run pre-commit again
- Manual fixes: Address remaining issues manually
- CI failures: Same checks run in CI—fix locally first
If pre-commit detects secrets:
- Verify it's a false positive: Some patterns may match non-secrets
- If real secret: Remove it immediately, rotate the credential
- Check git history: Use
git logto see if it was ever committed - Clean history if needed: Consider using
git filter-branchor BFG Repo-Cleaner
If an AI agent violates standards:
- Explicitly reference CONTEXT.md: "Please follow docs/ai/CONTEXT.md section X"
- Point to specific rules: Quote the exact standard being violated
- Re-run pre-commit: Quality gates will catch many violations
This framework is designed with security as the highest priority:
| Security Feature | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 🔐 Secrets Protection | ✅ Active | Comprehensive .gitignore prevents accidental secret commits |
| 🔍 Pre-commit Detection | ✅ Active | Pre-commit hooks detect secrets via detect-secrets.sh |
| 🔒 CI Secret Scanning | ✅ Active | Gitleaks scans full git history in CI (defense in depth) |
| 🛡️ SAST Scanning | ✅ Active | Semgrep performs static security analysis (OWASP, security audit) |
| 📦 Dependency Scanning | ✅ Active | OSV-Scanner checks dependencies for known vulnerabilities |
| 🛡️ Least Privilege | ✅ Active | All scripts should use least privilege principles |
| ✅ Input Validation | ✅ Active | All inputs should be treated as untrusted |
| 📋 Audit Trail | ✅ Active | Pre-commit logs and CI artifacts provide audit trails |
Do's ✅:
- ✅ Always use
.envfiles or secure secret management - ✅ Rotate credentials if a secret is ever exposed
- ✅ Review
.gitignoreto ensure all sensitive files are covered - ✅ Use example files to document required variables in
.env.example
Don'ts ❌:
- ❌ Never hardcode credentials
- ❌ Never log secrets
- ❌ Never commit
.envfiles or secrets
If you discover a security vulnerability in this framework:
- ❌ Do not open a public issue
- ✅ Contact the repository maintainers privately
- ✅ Include details about the vulnerability and potential impact
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0. See LICENSE for full text.
| File | Purpose | Status |
|---|---|---|
docs/ai/CONTEXT.md |
Authoritative AI behavior standards (mandatory for AI agents) | ✅ Required |
docs/requirements.md |
Project requirements and acceptance criteria | ✅ Required |
.gitignore |
Authoritative security rules (secrets, artifacts) | ✅ Required |
.pre-commit-config.yaml |
Quality check configuration | ✅ Required |
.github/workflows/ci.yaml |
CI/CD pipeline definition | ✅ Required |
scripts/run-precommit.sh |
Pre-commit execution wrapper (use this, not pre-commit directly) |
✅ Required |
scripts/detect-secrets.sh |
Secret detection script (runs automatically via pre-commit) | ✅ Required |
bootstrap-template-structure.sh |
Recreate template structure | ✅ Optional |
When contributing to this framework:
- Follow all standards in
docs/ai/CONTEXT.md - Ensure pre-commit passes:
./scripts/run-precommit.sh - Update documentation if adding new features
- Maintain backward compatibility where possible
- Test on both RHEL 9/10 and Ubuntu 22.04