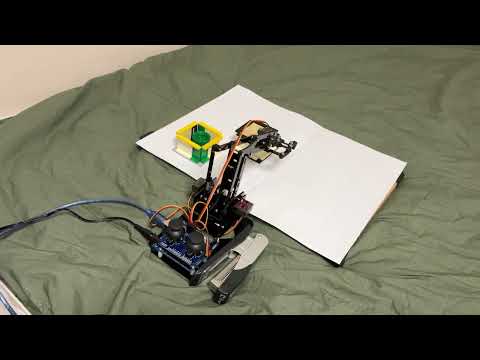
Project for a university graduation thesis in 2025.
This project implements a vision-based pick & place system for a meArm-style robotic arm using an ESP32 camera, OpenCV, homography calibration, and inverse kinematics.
Detected objects are converted from camera pixel coordinates into real-world coordinates, then into joint angles, and finally sent to an Arduino to physically move the robot arm.
💡 Click the image above to watch the full demonstration video on YouTube.
- ESP32 Camera WebServer image acquisition
- Perspective (homography) calibration from camera → real plane
- HSV-based color detection (green & black objects)
- Object filtering using area and circularity
- Inverse kinematics for a 3-DOF meArm-style robot
- Pick & place logic with predefined drop zones
- Optional P-control (proportional control) for smooth motion
- Serial communication with Arduino
ESP32 Camera
↓
CameraWebServer (image stream)
↓
PC (main control)
↓
a_*.py → Calibration & color tuning
↓
(b_color_detect_and_IK.py → Object detection & coordinate conversion)
↓
final_com_*.py → IK + motion planning (+ P-control)
↓
Serial (USB)
↓
Arduino (final_arm.ino)
↓
meArm Robot Arm
- meArm-style 4-DOF robotic arm with joystick
- Custom gripper (hardware folder)
*Print all .stl files inside hardware folder. Files labeled x2 require two copies.

- Arduino UNO
- SG90 or MG90 *4 (Base, Shoulder, Elbow, Claw)
- ESP32-CAM AI thinker
- Arduino cable (PC ↔ Arduino)
- Stable lighting (for color detection)
- Python 3.8+
- Arduino IDE
- Flash CameraWebServer example to the ESP32-CAM
Enter the Wi-Fi name and password intoCameraWebServer.ino. - Confirm live image access via browser
- ESP32-CAM should be able to see robot arm and workspace entirely
(I used two sheets of white A4 paper stacked together as my workspace.)
# Example:
http://192.168.x.xxx
First, measure your workspace in mm then fill real_pts
And Run:
python a_calibrate_homography.py-
Click 4 corner points of workspace in this order:
- Top-Left
- Top-Right
- Bottom-Left
- Bottom-Right
-
A
homography_matrix.jsonfile will be generated
This maps camera pixels → real-world coordinates (mm).
Tune HSV values for your environment:
python a_hsv_tuner.py- Adjust trackbars until the object is white and the background black
- Copy the printed HSV ranges into the detection scripts if needed
python b_color_detect_and_IK.py- Detects objects
- Converts to robot coordinates
- Calculates joint angles (no physical movement)
Useful for debugging geometry before motion.
- Open
final_arm.inoin Arduino IDE - Upload to Arduino
- Confirm servo directions and neutral positions
python final_com_no_PID.pypython final_com_with_P.pyControls:
- Enter → start pick & place
- q → quit program
-
Inverse Kinematics
- 2-link planar arm (L1, L2)
- Base rotation + shoulder + elbow
-
P-Control (final_com_with_P.py)
- Smooth joint interpolation
- Adjustable
Kp, speed limits, and thresholds
-
Pick Strategy
- Horizontal side approach
- Slide motion toward object
- Lift → move → drop → return home
Predefined joint angles for sorting:
DROP_GREEN = (base, shoulder, elbow)
DROP_BLACK = (base, shoulder, elbow)These can be customized per setup. Use robotarm_manual to copy the angles
- Lighting stability is critical for HSV detection
- Calibrate homography after camera position is fixed
- Servo offsets must be tuned per robot
This project is released under the MIT License. Feel free to use, modify, and share.
- OpenCV
- ESP32 CameraWebServer example
- meArm community