Author: Jason Tang
A comprehensive LLM-powered Binary Ninja plugin for intelligent binary analysis and reverse engineering.
BinAssist is an advanced LLM plugin designed to enhance binary analysis and reverse engineering workflows through intelligent automation. It leverages local and remote LLM capabilities to provide context-aware assistance throughout the binary analysis process. It supports fully agentic reverse engineering through its MCP client and MCP servers like BinAssistMCP
The plugin supports any OpenAI v1-compatible or Anthropic API, making it compatible with popular LLM providers including Ollama, LM Studio, Open-WebUI, OpenAI, Anthropic, AWS Bedrock (via LiteLLM), and others.
Recommended models:
- With Reasoning Support: Claude Sonnet 4+, OpenAI o1/o3/gpt-5, GPT-OSS (supports extended thinking for complex analysis)
- General Purpose: DeepSeek, LLaMA-based coder models, Claude Sonnet 3.5, GPT-4
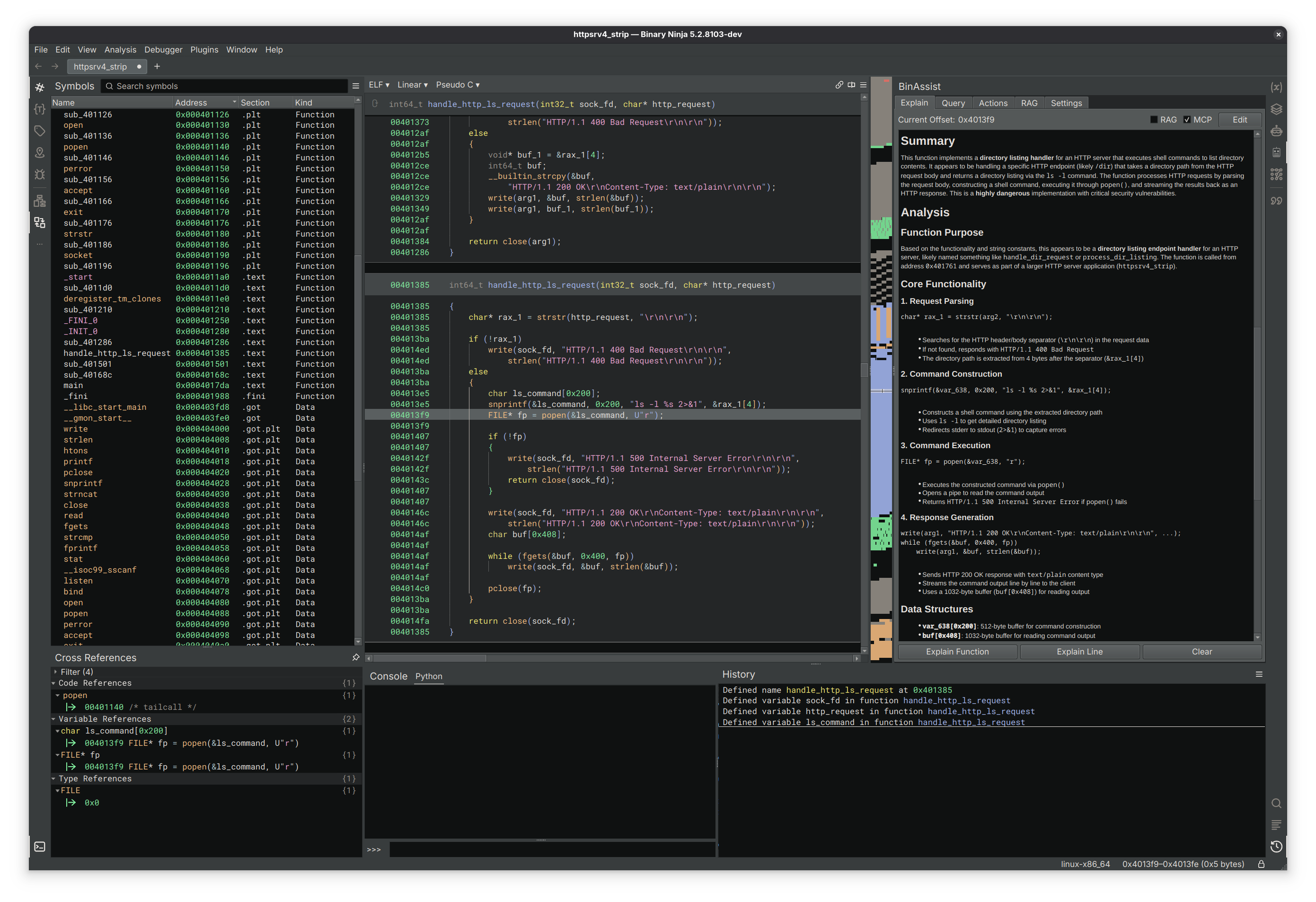
- Function Analysis: Comprehensive analysis of functions at all IL levels (LLIL, MLIL, HLIL)
- Instruction Analysis: Detailed explanations of individual instructions and their purpose
- Context-Aware: Stores responses at a function level, allowing you to easily keep track
- Edit Responses: Tweak the response as needed and save it for later
- Interactive LLM Chat: Direct conversation interface with the LLM
- ReAct Agent: Autonomous multi-step reasoning and analysis using the ReAct (Reasoning + Acting) framework
- Iterative problem-solving with reflection and self-correction
- Automatic tool selection and execution via MCP
- Step-by-step reasoning traces for transparency
- Up to 15 iterations with intelligent termination
- Extended Thinking: Support for reasoning effort control on compatible models
- Configurable thinking depth (None, Low, Medium, High)
- Compatible with Claude Sonnet 4+, OpenAI o1/o3/gpt-5, and gpt-oss
- Increases analysis quality for complex reverse engineering tasks
- Binary Context: Automatically includes relevant binary information in queries
- Flexible Prompting: Support for custom queries and analysis requests
- Streaming Responses: Real-time response generation with cancellation support
- Intelligent Suggestions: LLM-powered recommendations for improving binary analysis
- Four Action Types:
- Rename Function: Suggest semantically meaningful function names
- Rename Variable: Propose descriptive variable names based on usage
- Retype Variable: Recommend appropriate data types for variables
- Auto Create Struct: Generate structure definitions from data patterns
- Confidence Scoring: Each suggestion includes confidence metrics (0.0-1.0)
- Selective Application: Choose which suggestions to apply via interactive UI
- Status Tracking: Real-time feedback on action application success/failure
- Tool-Based Architecture: Uses native LLM tool calling for precise suggestions
- GraphRAG Architecture: Graph-based Retrieval-Augmented Generation for binary analysis
- ReIndex Binary: Build a semantic graph of all functions with call relationships
- Semantic Analysis: LLM-powered function summarization and categorization
- Automatic purpose inference from function names and behavior
- Security flag detection (network, file I/O, crypto, etc.)
- Activity profiling and risk assessment
- Security Analysis: Taint analysis for vulnerability detection
- Source-to-sink path finding (e.g.,
recv→strcpy) - Automatic detection of dangerous API usage patterns
- TAINT_FLOWS_TO and VULNERABLE_VIA edge creation
- Source-to-sink path finding (e.g.,
- Community Detection: Function clustering using Label Propagation algorithm
- Groups related functions based on call relationships
- Automatic module/purpose inference (Network I/O, Crypto, File Operations, etc.)
- Runs automatically after ReIndex completes
- Visual Graph View: Interactive visualization of function relationships
- Full-Text Search: FTS5-powered search across function names and summaries
- Query Tools: MCP-exposed tools for LLM to query the semantic graph
- ReAct Autonomous Agent: Full implementation of the ReAct framework for multi-step analysis
- Extended Thinking/Reasoning Effort: Provider-agnostic reasoning control for deeper analysis
- Anthropic: Extended thinking with configurable token budgets (2K-25K tokens)
- OpenAI: Reasoning effort levels for o1/o3/gpt-5 models
- Ollama: Native thinking parameter support for compatible models (gpt-oss)
- Function Calling: LLM can directly interact with Binary Ninja API to navigate and modify analysis
- MCP Integration: Model Context Protocol support for extensible tool integration
- RLHF Dataset Generation: Collect interaction data to enable model fine-tuning
- RAG Augmentation: Enhance queries with relevant documentation and context
- Async Processing: Non-blocking UI with background LLM processing
- Streaming Support: Real-time response generation with proper cancellation
- Flexible API Configuration: Support for multiple LLM providers and endpoints
- Model Selection: Choose from available models for different analysis tasks
- Reasoning Effort Control: Session-specific thinking depth configuration
- Adjustable per-query or globally in Settings tab
- Four levels: None (standard), Low (~2K tokens), Medium (~10K), High (~25K)
- Cost and latency warnings for higher levels
- Token Limits: Configurable maximum tokens for cost and performance optimization
- Database Management: Built-in RLHF and RAG database configuration
- Thread Safety: Proper async handling for Binary Ninja's threading requirements
- Model Fine-tuning: Leverage collected RLHF data for specialized model training
- Collaborative Features: Share analysis insights and suggestions across teams
- Hierarchical Communities: Multi-level community detection for large binaries
- Domain-Specific Models: Fine-tuned models for specific binary types
- Code Generation: Automated exploit development and patching suggestions
- Enhanced Vulnerability Detection: Expanded taint analysis with data flow tracking
- Performance Optimization: Enhanced suggestion accuracy and speed
# Install dependencies from the plugin directory
pip install -r requirements.txt- Open Settings → BinAssist in Binary Ninja
- Configure your LLM provider:
- API Host: Point to your preferred API endpoint (e.g.,
http://localhost:11434for Ollama) - API Key: Set authentication key if required
- Model: Choose your preferred model (e.g.,
gpt-oss:20b,claude-sonnet-4-5,o1-preview)
- API Host: Point to your preferred API endpoint (e.g.,
- Set database paths for RLHF and RAG features
- Adjust token limits based on your needs
- Configure Reasoning Effort in the Settings tab for models that support extended thinking
- Load a binary in Binary Ninja
- Click the 🤖 robot icon in the sidebar to open BinAssist
- Navigate between tabs based on your analysis needs:
- Explain: Analyze functions and instructions
- Query: Interactive chat with the LLM
- Actions: Get intelligent improvement suggestions
- Semantic Graph: Build and explore the binary's semantic graph
- RAG: Manage external documentation for context
Function Analysis:
- Navigate to a function in Binary Ninja
- Switch to the Explain tab
- Click "Explain Function" for comprehensive analysis
Getting Suggestions:
- Go to the Actions tab
- Select desired action types (Rename Function, etc.)
- Click "Analyse" to get LLM-powered suggestions
- Review confidence scores and apply selected actions
Interactive Queries:
- Use the Query tab for free-form questions
- Ask about specific functions, algorithms, or analysis techniques
- The LLM has full context of your current binary
Agentic Analysis (ReAct):
- Enable Agentic mode in the Query tab
- Enable MCP to provide tools for autonomous exploration
- Ask complex questions like "What does this binary do?" or "Find security vulnerabilities"
- Watch as the agent autonomously:
- Decompiles and analyzes functions
- Follows cross-references
- Builds understanding through iterative reasoning
- Provides comprehensive analysis with step-by-step traces
Semantic Graph Analysis:
- Go to the Semantic Graph tab
- Click "ReIndex Binary" to build the function graph
- Community detection runs automatically after indexing
- Use "Semantic Analysis" for LLM-powered function summaries
- Run "Security Analysis" to find vulnerable source→sink paths
- Explore the Visual Graph to see function relationships
- Use Search to find functions by name or summary content
https://github.com/jtang613/BinAssist
- Model-View-Controller (MVC): Clean separation of concerns across all tabs
- Service-Oriented Architecture: Modular services for different analysis tasks
- Observer Pattern: Qt signal-slot communication for responsive UI
- Async/Await: Non-blocking operations with proper thread management
Controllers:
ExplainController: Manages function and instruction analysisQueryController: Handles interactive LLM conversationsActionsController: Coordinates intelligent suggestion generationSemanticGraphController: Orchestrates GraphRAG indexing and analysis
Services:
BinaryContextService: Extracts and formats binary informationActionsService: Validates and applies code improvementsRLHFService: Manages training data collectionRAGService: Handles document retrieval and context enhancementGraphRAGService: Manages semantic graph indexing and queriesGraphStore: SQLite-backed graph node and edge storageCommunityDetector: Label Propagation algorithm for function clusteringTaintAnalyzer: Source-to-sink vulnerability path detection
Threading:
ExplainLLMThread: Background processing for explanationsQueryLLMThread: Async chat processing with streamingActionsLLMThread: LLM tool calling for suggestion generationReActOrchestratorThread: Autonomous multi-step agent execution
Tools & Integration:
- MCP Tools: Native LLM tool calling for precise actions
- Binary Ninja API: Direct integration with analysis engine
- OpenAI Compatibility: Works with any OpenAI v1-compatible endpoint
- Binary Ninja: Version 4000 or higher
- Python: 3.8+ with Binary Ninja's Python environment
- Memory: 4GB+ recommended for local LLM usage
- Storage: ~100MB for plugin + model-dependent storage
Linux (Primary Development Platform)
- Fully tested and supported
- Recommended for production use
Windows
- Should work but less tested
- Submit issues for Windows-specific problems
macOS
- Should work but less tested
- Submit issues for macOS-specific problems
Local LLMs (Recommended):
# Ollama setup
curl -fsSL https://ollama.ai/install.sh | sh
# Pull a general-purpose model
ollama pull llama3.1:8b
# Or pull a reasoning model (recommended for complex analysis)
ollama pull gpt-oss:20b
ollama serve # Runs on http://localhost:11434Other Compatible Providers:
- LM Studio: Desktop GUI for local models
- Ollama: Advanced local LLM interface CLI
- Open-WebUI: Advanced local LLM interface GUI
- OpenAI API: Cloud-based (requires API key)
- Anthropic API: Cloud-based (requires API key)
- LiteLLM Proxy: Access AWS Bedrock, Azure, and 100+ providers
- OpenRouter: Access to multiple models via API
-
Install Dependencies:
cd /path/to/BinAssist2 pip install -r requirements.txt -
Configure Binary Ninja:
- Install as a plugin in Binary Ninja's plugin directory
- Or run directly from development directory
-
Set up LLM Provider:
- Configure your preferred provider (see LLM Provider Setup above)
- Update BinAssist settings with correct API endpoints
Required Python Packages:
openai # OpenAI and LiteLLM provider API
anthropic # Anthropic Claude API
pysqlite3 # Database operations
markdown # Documentation formatting
httpx # HTTP client for API calls
anyio>=4.6 # Async I/O support
mcp # Model Context Protocol client
whoosh # Full-text search for RAG documents
We welcome contributions! Please see our contributing guidelines:
- Bug Reports: Submit detailed issues with reproduction steps
- Feature Requests: Propose new functionality with clear use cases
- Code Contributions: Follow existing patterns
- GitHub Issues: Primary support channel for bugs and features
This plugin is released under the MIT License - see LICENSE file for details.
Minimum Binary Ninja Version: 5000
Metadata Version: 2