Before starting the workshop, it is recommended to fork this repository into your own GitHub account. This allows you to work independently and save your progress.
After forking, you must configure the values in values.yaml with your personal OpenShift namespace and registry information. By default, the configuration uses maximilianopizarro5-dev as the namespace. You should update these values in the values.yaml file.
Before installing the chart, you need to configure the following values in values.yaml:
# Namespace configuration
namespace: <YOUR-NAMESPACE> # Replace with your OpenShift namespace (e.g., yourusername-dev)
# Pipeline configuration
pipeline:
# Source image in OpenShift internal registry
sourceImage: image-registry.openshift-image-registry.svc:5000/<YOUR-NAMESPACE>/workshop-pipelines:latest
# Target image in external registry (e.g., Quay.io)
targetImage: quay.io/<YOUR-QUAY-USERNAME>/workshop-pipelines
# Route configuration
route:
enabled: true
host: workshop-pipelines-<YOUR-NAMESPACE>.apps.rm2.thpm.p1.openshiftapps.comExample configuration:
namespace: maximilianopizarro5-dev
pipeline:
sourceImage: image-registry.openshift-image-registry.svc:5000/maximilianopizarro5-dev/workshop-pipelines:latest
targetImage: quay.io/maximilianopizarro/workshop-pipelines
route:
enabled: true
host: workshop-pipelines-maximilianopizarro5-dev.apps.rm2.thpm.p1.openshiftapps.comThis step is essential to ensure that all routes, URLs, and deployments work correctly in your personal Developer Sandbox environment.
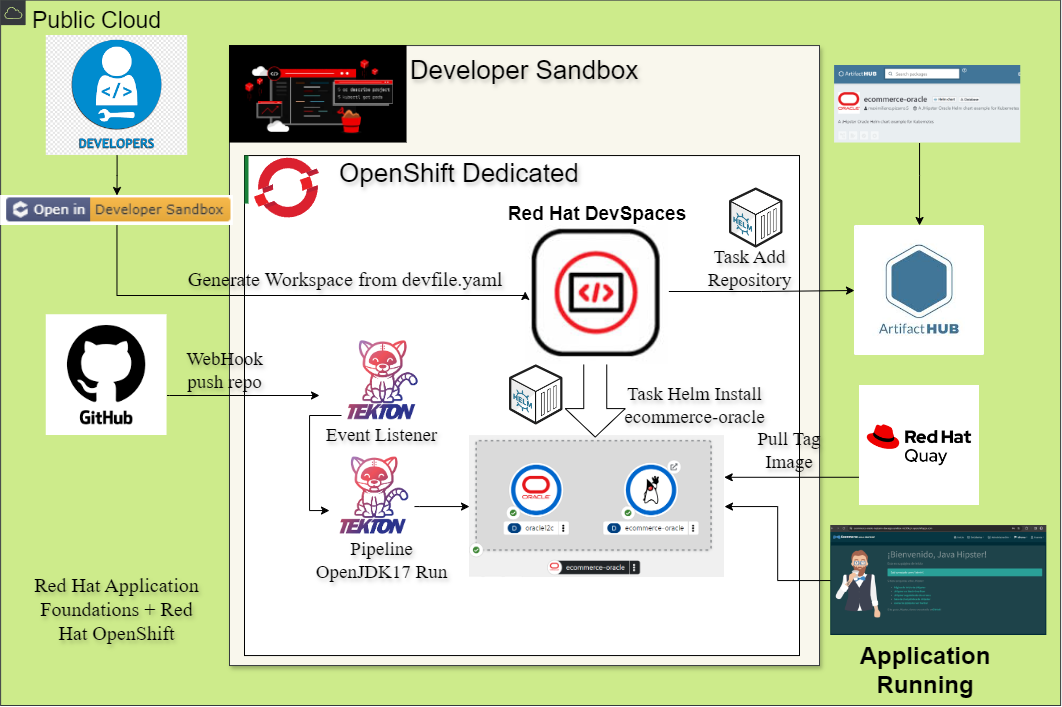
OpenShift Pipelines is a Kubernetes-native CI/CD solution based on Tekton. It allows you to define and run build, test, and deployment workflows using custom resources. Pipelines are composed of several objects:
- Pipeline: Defines the sequence of tasks to execute.
- PipelineRun: An instance of a Pipeline execution.
- Task: A reusable step in a pipeline (e.g., build, test, deploy).
- TaskRun: An instance of a Task execution.
- PipelineResource: Defines resources (e.g., Git repositories, images) used by tasks.
- TriggerTemplate: Template for creating PipelineRuns from events.
- TriggerBinding: Maps event parameters to PipelineRun parameters.
- EventListener: Listens for external events (e.g., GitHub webhook) and triggers pipelines.
In this Helm chart, the template includes objects related to pipelines such as Pipeline, PipelineRun, Task, EventListener, and TriggerTemplate to automate the CI/CD process for your application.
To deploy this example, you need a free subscription to Red Hat Developer Sandbox. Register with your Red Hat account to access an OpenShift environment for testing and development.
You can set up and deploy this project directly from OpenShift Dev Spaces, a cloud-based development environment integrated with OpenShift. Dev Spaces provides a pre-configured workspace and automates common development tasks using the devfile.yaml included in this repository.
The devfile.yaml defines a comprehensive set of tasks that streamline the deployment, management, and cleanup of the application and its supporting services. These tasks are accessible from the Dev Spaces workspace interface under the "Run Tasks" menu.
-
1. Helm repo add
Adds theworkshop-pipelinesHelm chart repository to your environment, making the chart available for installation. -
2. Helm install workshop-pipelines
Installs the main e-commerce application using theworkshop-pipelinesHelm chart from the packaged version (0.1.6) in thedocs/directory. -
3. Helm uninstall workshop-pipelines
Uninstalls theworkshop-pipelinesHelm chart, removing the deployed application and its resources. -
4. Helm upgrade workshop-pipelines local
Upgrades the installed chart to your local development version. This allows you to test changes without uninstalling and reinstalling. Note: You can skip step 3 and go directly from step 2 to step 4 to upgrade without uninstalling. -
a. Install Package of the application
Installs all required npm packages for the application located in the/appdirectory. -
b. Start Ecommerce
Starts the backend e-commerce application using Maven Wrapper (./mvnw). -
5. Helm add repo Developer Hub
Adds the official OpenShift Helm charts repository, which includes the Red Hat Developer Hub chart. -
6. Helm install Developer Hub v1.7.0
Installs the Red Hat Developer Hub using Helm, applying custom values fromvalues.yaml. -
c. Helm package workshop-pipelines
Packages the Helm chart forworkshop-pipelines, builds dependencies, and updates the local Helm repository index. -
7. Helm uninstall Developer Hub
Uninstalls the Red Hat Developer Hub from your environment.
- Open the workspace in OpenShift Dev Spaces using the provided link.
- In the workspace, click on Workspace > Run Tasks.
- Select the desired task from the list. Each task executes the corresponding commands and scripts defined in
devfile.yaml. - Monitor the output in the integrated terminal or output pane.
Each task is modular and can be run independently or in sequence, allowing you to deploy, configure, and clean up resources as needed for your development
View the OpenShift Topology.
Access the Web App Home Page.
Get the Web App route with the following command:
oc get routes workshop-pipelinesOutput
workshop-pipelines (main) $ oc get routes workshop-pipelines.
NAME HOST/PORT PATH SERVICES PORT TERMINATION WILDCARD
workshop-pipelines workshop-pipelines-maximilianopizarro5-dev.apps.rm2.thpm.p1.openshiftapps.com workshop-pipelines http edge/Redirect NoneAccess the WebHook settings and configure the ci-github route.
oc get routes ci-githubOutput
workshop-pipelines (main) $ oc get routes ci-github
NAME HOST/PORT PATH SERVICES PORT TERMINATION WILDCARD
ci-github ci-github-mpizarro-dev.apps.rm2.thpm.p1.openshiftapps.com el-ci-github http-listener edge/Redirect NoneThe pipeline includes a promote-to-quay task that copies images from the OpenShift internal registry to Quay.io. To enable this functionality, you need to:
- Create a repository in Quay.io
- Create a robot account with write permissions
- Configure the secret in your OpenShift namespace
- Update the
values.yamlfile with your credentials
- Log in to Quay.io with your account
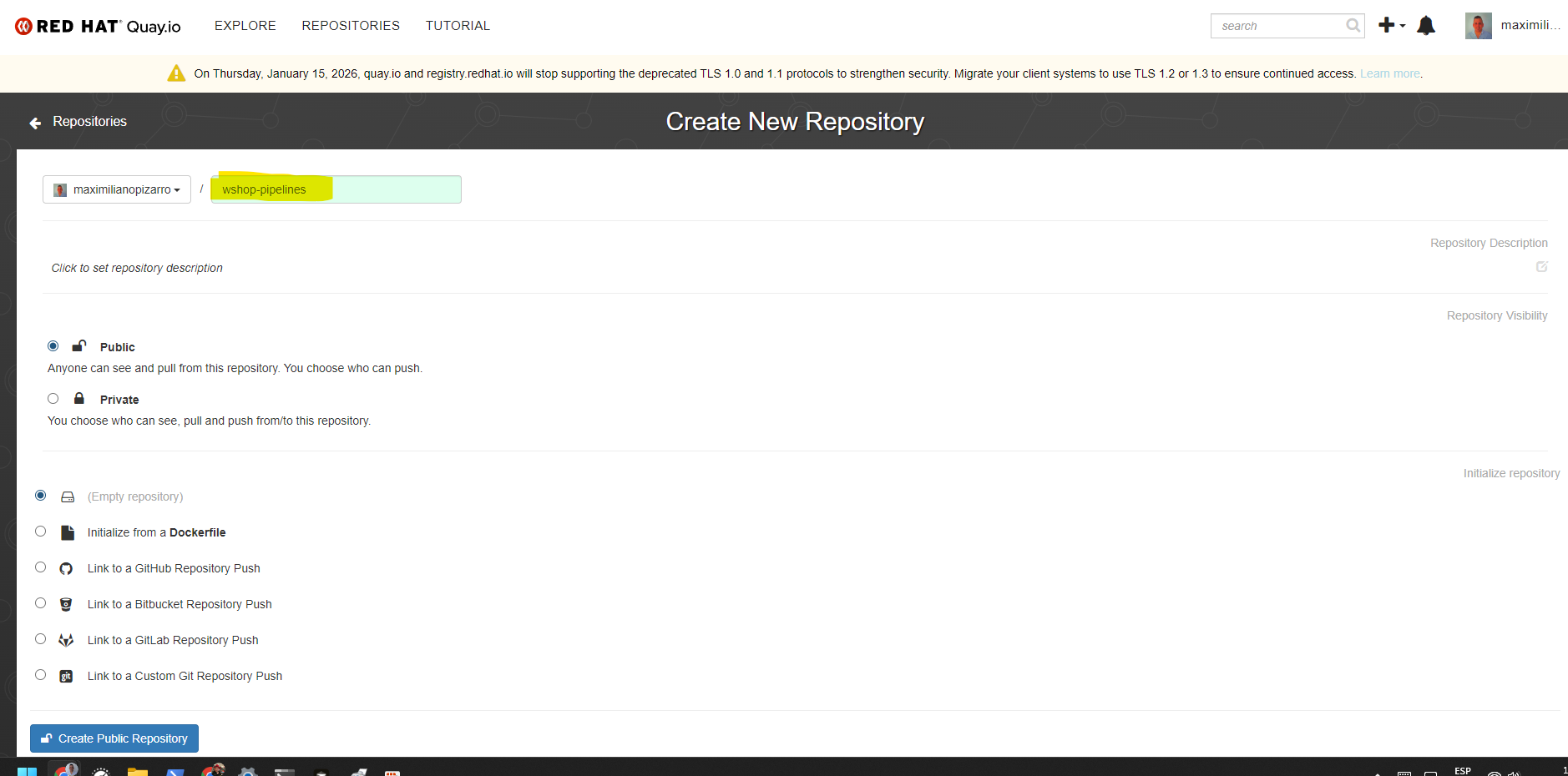
- Click on Create New Repository (or navigate to your organization/user account)
- Fill in the repository details:
- Repository Name:
workshop-pipelines(or your preferred name) - Visibility: Choose Public or Private based on your needs
- Description: Optional description for your repository
- Repository Name:
- Click Create Public Repository (or Create Private Repository)
A robot account is a special type of account designed for automated access to Quay.io repositories. It's more secure than using your personal credentials.
- In your Quay.io account, navigate to Account Settings (click on your username in the top right)
- Go to Robot Accounts in the left sidebar
- Click Create Robot Account
- Enter a name for the robot account (e.g.,
workshop-pipelines) - Click Create Robot Account
- After creating the robot account, you'll see it listed under Robot Accounts
- Click on the robot account name to view its details
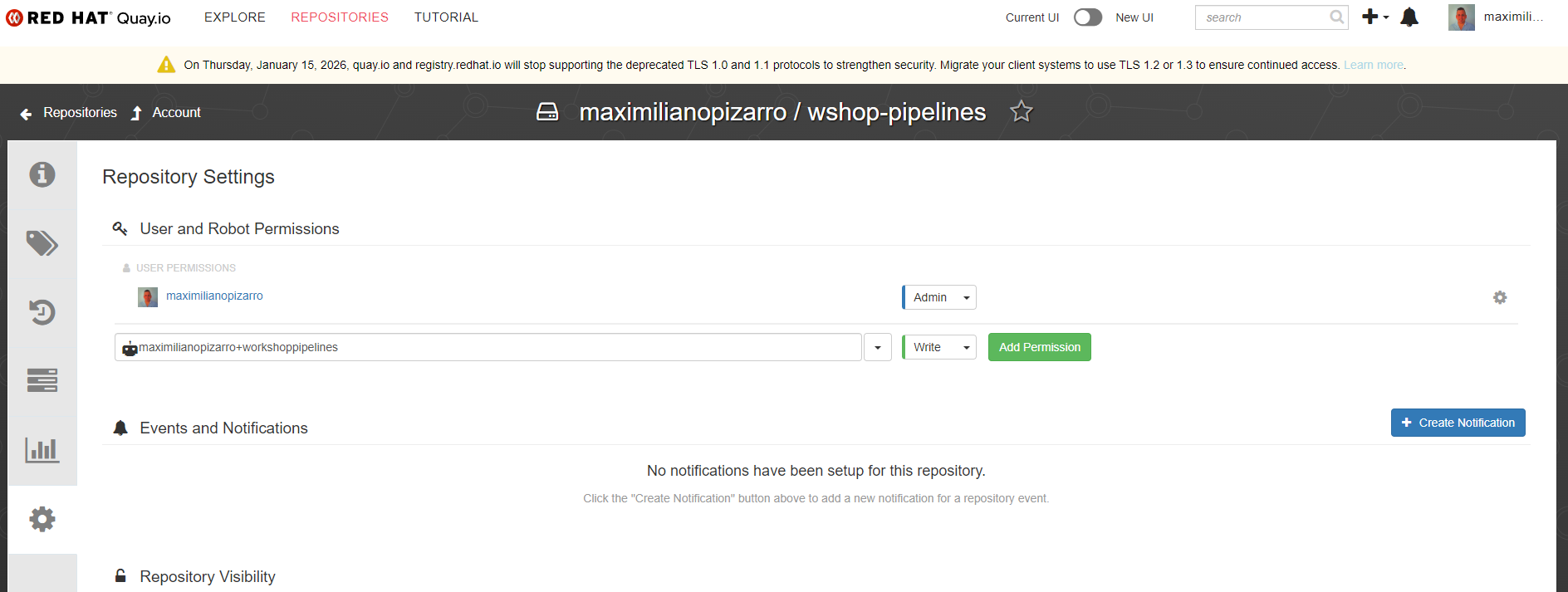
- In the Repository Permissions section, click Add Permission
- Select your repository (
workshop-pipelines) - Set the permission level to Write (this allows the robot to push images)
- Click Add Permission
- On the robot account details page, you'll see the credentials:
- Robot Username: This will be in the format
<your-username>+<robot-name>(e.g.,maximilianopizarro+workshoppipelines) - Robot Password: Click Regenerate Token if needed, then copy the password
- Robot Username: This will be in the format
- Important: Save these credentials securely. You'll need them for the next step.
Update your values.yaml file with the Quay.io configuration:
pipeline:
# Target image in external registry (e.g., Quay.io)
targetImage: quay.io/<YOUR-QUAY-USERNAME>/workshop-pipelines
# Quay.io secret configuration for promote-to-quay task
quaySecret:
# Secret name (must match the pattern: <quay-username>-workshoppipelines-pull-secret)
name: <YOUR-QUAY-USERNAME>-workshoppipelines-pull-secret
# Quay.io robot account username (format: username+robotname)
username: "<YOUR-USERNAME>+<ROBOT-NAME>"
# Quay.io robot account password (from Step 4)
password: "<ROBOT-ACCOUNT-PASSWORD>"
# Email for docker registry secret
email: "<YOUR-EMAIL>"Example:
pipeline:
targetImage: quay.io/maximilianopizarro/workshop-pipelines
quaySecret:
name: maximilianopizarro-workshoppipelines-pull-secret
username: "maximilianopizarro+workshoppipelines"
password: "PASSWORD-ROBOT"
email: "maximiliano.pizarro.5@gmail.com"When you install or upgrade the Helm chart, it will automatically create the Docker registry secret in OpenShift using the credentials from values.yaml:
helm install workshop-pipelines . -f values.yamlor
helm upgrade workshop-pipelines . -f values.yamlThe secret will be created automatically if pipeline.quaySecret.username and pipeline.quaySecret.password are provided in values.yaml.
After installing the chart, verify that the secret was created:
oc get secret <YOUR-QUAY-USERNAME>-workshoppipelines-pull-secret -n <YOUR-NAMESPACE>The promote-to-quay task in the pipeline will automatically:
- Authenticate with Quay.io using the robot account credentials from the secret
- Authenticate with the OpenShift internal registry using the service account token
- Copy the image from the internal registry to Quay.io after a successful build
The task runs after the s2i-binary-build task completes successfully, ensuring images are only promoted when the build succeeds.
See the pipelines.
Review the documentation.
See the App Topology.
See the Web App Logs.
Open the OpenShift Web Terminal and run:
helm repo add openshift-helm-charts https://charts.openshift.io/Output:
bash-5.1 ~ $ helm repo add openshift-helm-charts https://charts.openshift.io/
WARNING: Kubernetes configuration file is group-readable. This is insecure. Location: /home/user/.kube/config
WARNING: Kubernetes configuration file is world-readable. This is insecure. Location: /home/user/.kube/config
"openshift-helm-charts" has been added to your repositorieshttps://github.com/settings/developers
-->developer-hub/app-config-rhdh.yaml
...
github:
development:
clientId: <<CLIENT-ID>>
clientSecret: <<CLIENT-SECRET>>
...-->developer-hub/app-config-rhdh.yaml
...
baseUrl: <<URL>> https://redhat-developer-hub- <NAMESPACE> .apps.rm2.thpm.p1.openshiftapps.com/
...Example:
...
baseUrl: <<URL>> https://redhat-developer-hub-maximilianopizarro5-dev.apps.rm2.thpm.p1.openshiftapps.com/
...Install the chart:
helm install redhat-developer-hub openshift-helm-charts/redhat-developer-hub -f developer-hub/values.yaml --version 1.2.2Access the Developer Portal with GitHub access.
Register the WorkShop Pipelines component:
https://github.com/maximilianoPizarro/workshop-pipelines/blob/main/catalog-info.yamlhelm repo add workshop-pipelines https://maximilianopizarro.github.io/workshop-pipelines/helm install workshop-pipelines workshop-pipelines/workshop-pipelines --version "VERSION" --set route.host=workshop-pipelines-<NAMESPACE>.apps.rm2.thpm.p1.openshiftapps.comExample:
helm install workshop-pipelines workshop-pipelines/workshop-pipelines --version 0.1.6helm uninstall workshop-pipelines