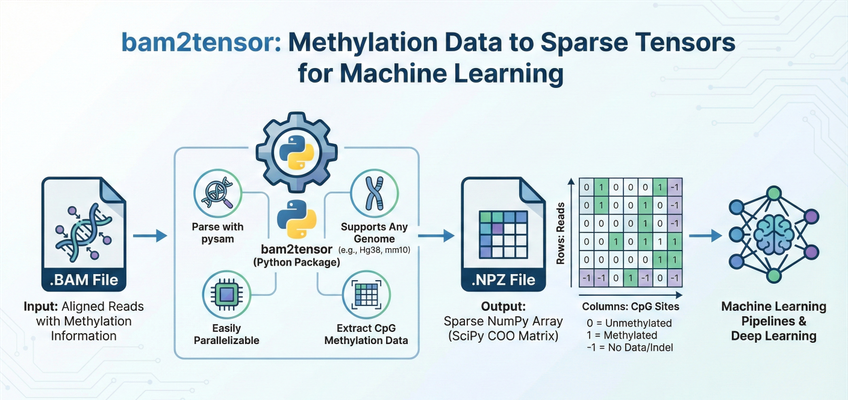
bam2tensor is a Python package for converting bisulfite-sequencing .bam files to sparse tensor representations of DNA methylation data. It extracts read-level methylation states from CpG sites and outputs efficient sparse COO matrices as .npz files, ready for deep learning pipelines.
- Features
- Requirements
- Installation
- Quick Start
- Usage
- Output Data Structure
- Supported Aligners
- Performance Tips
- API Reference
- Contributing
- License
- Credits
- BAM Parsing: Efficiently parses
.bamfiles using pysam - Complete CpG Extraction: Extracts methylation data from all CpG sites genome-wide
- Multi-Genome Support: Works with any reference genome (GRCh38/hg38, T2T-CHM13, mm10, etc.)
- Sparse Storage: Stores data in sparse COO matrix format for memory-efficient loading
- NumPy/SciPy Integration: Exports to
.npzfiles compatible with NumPy and SciPy - Efficient Algorithm: Linear-scan algorithm ensures minimal memory usage with no read duplication
- Batch Processing: Process multiple BAM files with directory recursion
- Caching: CpG site indexing is cached to accelerate repeated runs on the same genome
- Quality Filtering: Configurable mapping quality thresholds
- Python 3.10 or higher
- A reference genome FASTA file (must match the genome used for alignment)
- Indexed BAM files (
.bamwith corresponding.bam.baiindex files)
Core dependencies are automatically installed:
pysam- BAM file handlingbiopython- FASTA parsingscipy- Sparse matrix operationsnumpy- Numerical operationsclick- Command-line interfacetqdm- Progress bars
pip install bam2tensorgit clone https://github.com/mcwdsi/bam2tensor.git
cd bam2tensor
pip install .git clone https://github.com/mcwdsi/bam2tensor.git
cd bam2tensor
pip install poetry
poetry install# Basic usage with a single BAM file
bam2tensor \
--input-path sample.bam \
--reference-fasta GRCh38.fa \
--genome-name hg38
# This creates: sample.methylation.npzProcess a single bisulfite-sequencing BAM file:
bam2tensor \
--input-path /path/to/aligned_reads.bam \
--reference-fasta /path/to/reference.fa \
--genome-name hg38This will:
- Parse the reference FASTA to identify all CpG sites (cached for future runs)
- Extract methylation states from each read in the BAM file
- Output a sparse matrix to
aligned_reads.methylation.npz
Process all BAM files in a directory recursively:
bam2tensor \
--input-path /path/to/bam_directory/ \
--reference-fasta /path/to/reference.fa \
--genome-name hg38 \
--verboseEach BAM file will generate a corresponding .methylation.npz file in the same location.
For non-human genomes or custom chromosome sets:
# Mouse genome (mm10)
bam2tensor \
--input-path mouse_sample.bam \
--reference-fasta mm10.fa \
--genome-name mm10 \
--expected-chromosomes "chr1,chr2,chr3,chr4,chr5,chr6,chr7,chr8,chr9,chr10,chr11,chr12,chr13,chr14,chr15,chr16,chr17,chr18,chr19,chrX,chrY"
# T2T-CHM13 human genome
bam2tensor \
--input-path sample.bam \
--reference-fasta chm13v2.0.fa \
--genome-name T2T-CHM13 \
--expected-chromosomes "chr1,chr2,chr3,chr4,chr5,chr6,chr7,chr8,chr9,chr10,chr11,chr12,chr13,chr14,chr15,chr16,chr17,chr18,chr19,chr20,chr21,chr22,chrX,chrY"Usage: bam2tensor [OPTIONS]
Extract read-level methylation data from an aligned .bam file and export
the data as a SciPy sparse matrix.
Options:
--version Show the version and exit.
--input-path PATH Input .bam file OR directory to recursively
process. [required]
--genome-name TEXT A custom string referring to your genome
name, used to save a cache file (e.g. hg38,
hg38-no-alt, etc.). [required]
--expected-chromosomes TEXT A comma-separated list of chromosomes to
expect in the .fa genome. Defaults to hg38
chromosomes (chr1-chr22, chrX, chrY).
--reference-fasta PATH Reference genome FASTA file (critical to
determine CpG sites). [required]
--quality-limit INTEGER Quality filter for aligned reads (default =
20).
--verbose Verbose output.
--skip-cache De-novo generate CpG sites (slow).
--debug Debug mode (extensive validity checking +
debug messages).
--overwrite Overwrite output file if it exists.
--help Show this message and exit.
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
--input-path |
Path to a single .bam file or a directory. If a directory is provided, all .bam files are processed recursively. |
--genome-name |
An identifier for your reference genome (e.g., hg38, mm10). Used to name the cache file for CpG site positions. |
--expected-chromosomes |
Comma-separated list of chromosome names to process. Chromosomes not in this list are skipped. Defaults to human autosomes + sex chromosomes. |
--reference-fasta |
Path to the reference genome FASTA file. Must match the genome used for alignment. |
--quality-limit |
Minimum mapping quality score (MAPQ) for reads to be included. Default is 20. |
--verbose |
Enable detailed progress output including per-chromosome progress bars. |
--skip-cache |
Force regeneration of CpG site cache. Useful if you've modified the reference or chromosome list. |
--debug |
Enable extensive validation and debug output. Slower but useful for troubleshooting. |
--overwrite |
Overwrite existing .methylation.npz files. Without this flag, existing outputs are skipped. |
bam2tensor generates one .npz file per input BAM file. Each file contains a SciPy sparse COO matrix with the following structure:
| Dimension | Represents |
|---|---|
| Rows | Unique reads (primary alignments that pass quality filters) |
| Columns | CpG sites (ordered by genomic position across all chromosomes) |
| Value | Meaning |
|---|---|
1 |
Methylated (cytosine preserved as C) |
0 |
Unmethylated (cytosine converted to T by bisulfite treatment) |
-1 |
No data (indel, SNV, or site not covered by read) |
Note: Sparse matrices only store non-zero values. Positions with value 0 (unmethylated) are stored, but positions not covered by a read are simply absent from the matrix.
import scipy.sparse
import numpy as np
# Load the sparse matrix
methylation_matrix = scipy.sparse.load_npz("sample.methylation.npz")
print(f"Matrix shape: {methylation_matrix.shape}")
print(f"Number of reads: {methylation_matrix.shape[0]}")
print(f"Number of CpG sites: {methylation_matrix.shape[1]}")
print(f"Non-zero entries: {methylation_matrix.nnz}")
print(f"Sparsity: {1 - methylation_matrix.nnz / np.prod(methylation_matrix.shape):.4%}")For small regions or when dense operations are needed:
# Convert entire matrix to dense (warning: may use significant memory)
dense_matrix = methylation_matrix.toarray()
# Convert to CSR format for efficient row slicing
csr_matrix = methylation_matrix.tocsr()
# Get methylation data for reads 0-99
subset = csr_matrix[0:100, :].toarray()
# Convert to CSC format for efficient column slicing
csc_matrix = methylation_matrix.tocsc()
# Get data for CpG sites 1000-1099
cpg_subset = csc_matrix[:, 1000:1100].toarray()To map between matrix column indices and genomic coordinates, use the GenomeMethylationEmbedding class:
from bam2tensor.embedding import GenomeMethylationEmbedding
# Load or recreate the embedding used during extraction
embedding = GenomeMethylationEmbedding(
genome_name="hg38",
expected_chromosomes=["chr" + str(i) for i in range(1, 23)] + ["chrX", "chrY"],
fasta_source="/path/to/GRCh38.fa",
)
# Convert matrix column index to genomic position
chrom, pos = embedding.embedding_to_genomic_position(12345)
print(f"Column 12345 corresponds to {chrom}:{pos}")
# Convert genomic position to matrix column index
col_idx = embedding.genomic_position_to_embedding("chr1", 10525)
print(f"chr1:10525 is at column {col_idx}")
# Get total number of CpG sites
print(f"Total CpG sites: {embedding.total_cpg_sites:,}")import scipy.sparse
import numpy as np
# Load the data
matrix = scipy.sparse.load_npz("sample.methylation.npz")
csr = matrix.tocsr()
# Calculate per-CpG methylation rates (excluding -1 values)
methylation_rates = []
for cpg_idx in range(matrix.shape[1]):
col_data = csr.getcol(cpg_idx).toarray().flatten()
# Filter out -1 (no data) and positions with no coverage
valid_data = col_data[(col_data >= 0)]
if len(valid_data) > 0:
rate = np.mean(valid_data)
else:
rate = np.nan
methylation_rates.append(rate)
methylation_rates = np.array(methylation_rates)
print(f"Mean methylation rate: {np.nanmean(methylation_rates):.2%}")
print(f"CpG sites with coverage: {np.sum(~np.isnan(methylation_rates)):,}")import torch
import scipy.sparse
import numpy as np
# Load sparse matrix
matrix = scipy.sparse.load_npz("sample.methylation.npz")
# Convert to PyTorch sparse tensor
coo = matrix.tocoo()
indices = torch.LongTensor(np.vstack((coo.row, coo.col)))
values = torch.FloatTensor(coo.data)
shape = torch.Size(coo.shape)
sparse_tensor = torch.sparse_coo_tensor(indices, values, shape)
print(f"PyTorch sparse tensor shape: {sparse_tensor.shape}")
# For models that need dense input (specific region)
region_start, region_end = 0, 1000
dense_region = matrix.tocsc()[:, region_start:region_end].toarray()
dense_tensor = torch.FloatTensor(dense_region)bam2tensor supports BAM files from bisulfite-aware aligners that include strand information tags:
| Aligner | Tag | Values |
|---|---|---|
| Biscuit | YD |
f (forward/OT/CTOT), r (reverse/OB/CTOB) |
| gem3 / Blueprint | XB |
C (forward), G (reverse) |
These tags indicate which strand the original bisulfite-converted DNA came from, which is essential for correctly interpreting C/T as methylated/unmethylated.
-
Use the cache: The first run on a new genome builds a CpG site index, which is cached. Subsequent runs are much faster.
-
Process in parallel: bam2tensor processes one BAM at a time, but you can run multiple instances in parallel on different BAM files:
# Using GNU parallel find /data/bams -name "*.bam" | parallel -j 4 \ bam2tensor --input-path {} --reference-fasta ref.fa --genome-name hg38
-
Ensure BAM files are indexed: Each BAM file requires a corresponding
.bam.baiindex file. Create with:samtools index sample.bam
-
Use SSDs: Both reading BAM files and writing output benefit from fast storage.
-
Memory considerations: Memory usage scales with the number of CpG sites (columns) rather than reads. For human genomes (~28M CpG sites), expect moderate memory usage.
Main class for managing CpG site positions and coordinate conversions.
GenomeMethylationEmbedding(
genome_name: str, # Identifier for caching
expected_chromosomes: list, # List of chromosome names to process
fasta_source: str, # Path to reference FASTA
skip_cache: bool = False, # Force regeneration of cache
verbose: bool = False # Enable verbose output
)Key Methods:
embedding_to_genomic_position(embedding: int) -> tuple[str, int]- Convert column index to (chromosome, position)genomic_position_to_embedding(chrom: str, pos: int) -> int- Convert genomic position to column index
Key Attributes:
total_cpg_sites: int- Total number of CpG sites across all chromosomescpg_sites_dict: dict[str, list[int]]- Dictionary mapping chromosome names to lists of CpG positions
Core function for extracting methylation data from a BAM file.
extract_methylation_data_from_bam(
input_bam: str, # Path to BAM file
genome_methylation_embedding: GenomeMethylationEmbedding, # Embedding object
quality_limit: int = 20, # Minimum MAPQ
verbose: bool = False, # Enable verbose output
debug: bool = False # Enable debug output
) -> scipy.sparse.coo_matrixReturns: A SciPy COO sparse matrix with shape (n_reads, n_cpg_sites).
Contributions are welcome! Please see the Contributor Guide for guidelines on:
- Setting up a development environment
- Running tests
- Code style requirements
- Submitting pull requests
# Install development dependencies
poetry install
# Run all checks (linting, type checking, tests)
nox
# Run specific checks
nox --session=tests # Run pytest
nox --session=mypy # Type checking
nox --session=pre-commit # Linting
# Format code
poetry run black src tests
poetry run ruff check --fix src testsDistributed under the terms of the MIT license, bam2tensor is free and open source software.
If you encounter any problems, please file an issue with:
- A description of the problem
- Steps to reproduce
- Your Python version and operating system
- Relevant error messages or logs
This project is developed and maintained by Nick Semenkovich (@semenko), as part of the Medical College of Wisconsin's Data Science Institute.
This project was generated from Statistics Norway's SSB PyPI Template.