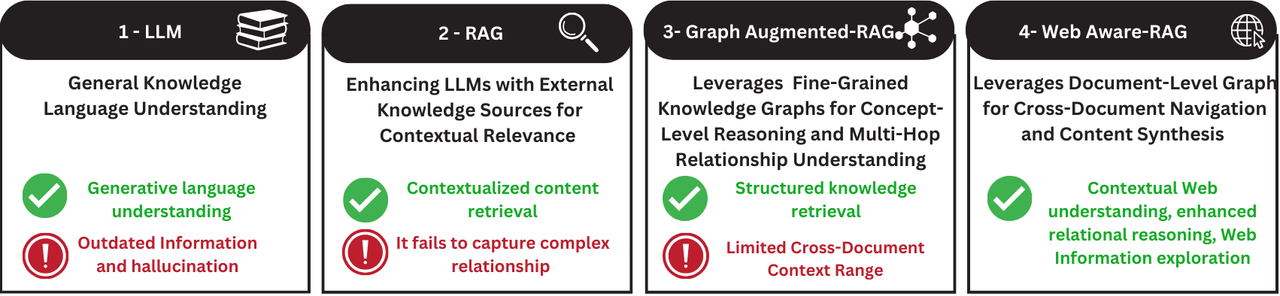
This repository contains the implementation of WebRAG, a Web-aware RAG system that enhances multi-hop question answering by integrating hyperlink-based document graph structures into the retrieval process.
The web is a vast and intricate network of interconnected information sources. While traditional web search engines have long enabled users to search through billions of linked pages using keyword matching, the emergence of Large Language Models (LLMs) marks a fundamental shift in how we search and process online information. Organizations are increasingly adopting LLM-based solutions, particularly Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG), to automate information extraction from web documents, moving beyond simple keyword matching to understand semantic relationships between content.
However, while RAG excels at reasoning within a single context window, it faces significant challenges in multi-hop reasoning, particularly in web search scenarios where information must be gathered and processed from different sources. Graph-augmented RAG address these limitations by leveraging graph-structured data to capture relationships between documents and enable more context-aware responses.
This work investigates whether LLMs enhanced with web document-level, graph-augmented RAG can better automate the process of navigating and synthesizing information from complex web documents. Our approach exploits both the textual content of web documents and their hyperlink structure to create a comprehensive framework for Web-based information navigation and synthesis. We evaluate our approach on benchmark multi-hop question-answering datasets, and demonstrate measurable improvements in retrieval performance for information synthesis when compared to baseline approaches.
- Constructs a hyperlink graph between documents (using links in web pages).
- Expands context retrieval by exploring the graph neighborhood of relevant pages.
- Merges retrieved text from both RAG and WebGraph modules to generate more accurate and context-rich answers.
- Designed for multi-hop question answering tasks.
- Evaluated on benchmark datasets: 2WikiMultiHopQA and HotpotQA.
- Outperforms standard RAG and shows strong performance compared to more complex graph-based methods.
├── Data/
│ ├── 2WikiMultihopQA/ # 2WikiMultiHopQA demo dataset files
│ └── HotpotQA/ # HotpotQA demo dataset files
│
├── RAG/ # Core RAG logic and helper modules
│ ├── __import__.py # Import handling (likely placeholder)
│ ├── __init__.py # Package initializer
│ ├── func.py # Utility functions
│ ├── rag.py # Main RAG implementation
│ ├── relatedData.py # Handles related data augmentation
│ └── SystemPrompts/ # System prompt templates
│ ├── prompt-2WikiMultihopQA.txt
│ └── prompt-HotpotQA.txt
│
├── eval.py # Evaluation logic (e.g., EM/F1 computation)
├── main.py # Script to run the pipeline
├── main.ipynb # Notebook for interactive exploration
├── README.md # Project documentation
├── requirements.txt # Python dependencies
└── .gitignore # Git ignore rulesWe use:
- 2WikiMultiHopQA: Focused on compositional reasoning over Wikipedia.
- HotpotQA: Natural multi-hop questions with supporting paragraphs.
Note: Please download the datasets and place them in the appropriate folders under the
Data/directory as described above.
- Clone the repository:
git clone https://github.com/mehrshaad/Multi-hop-WebRAG.git
cd Multi-hop-WebRAG- Install dependencies:
pip install -r requirements.txt- Download the datasets (or place them in the
data/directory).
Run the main script with:
python main.pyWebRAG demonstrates substantial improvements over baseline RAG on the HotpotQA dataset:
- EM: 80.0% (WebRAG) vs. 41.0% (RAG)
- F1: 82.2% (WebRAG) vs. 50.1% (RAG)


If you use WebRAG in your research, please cite our work:
@inproceedings{yourname2025webrag,
title={Enhancing Retrieval-Augmented Generation with Document Link Structure for Multi-hop Web Question Answering},
author={Sara Mazaheri, Ali Dadashzadeh, Arash Niroumand, Renata Dividino},
booktitle={LLMs Meet Dataset Workshop (LMD 20205). In conjunction with the 35th IEEE International Conference on Collaborative Advances in Software and Computing (CASCON 20205).}
publisher={IEEE},
year={2025}
}- Extend evaluation to more diverse, unstructured web sources.
- Improve graph construction beyond hyperlinks (e.g., semantic linking).
- Explore hybrid architectures combining different graph types.
- Investigate the use of advanced models such as Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) and DeepWalk to further enhance document graph representation and retrieval performance.
 Sara Mazaheri |
 Ali Dadashzadeh |
 Arash Niroumand |
 Renata Dividino |