🚀 Version 3.0 - Modern Python library (3.8+) with uv support! See docs/ for guides.
Show configuration parser (shconfparser) is a Python library for parsing network device configurations. This library examines the config and breaks it into a set of parent and clild relationships.
shconfparser is a vendor independent library where you can parse the following formats:
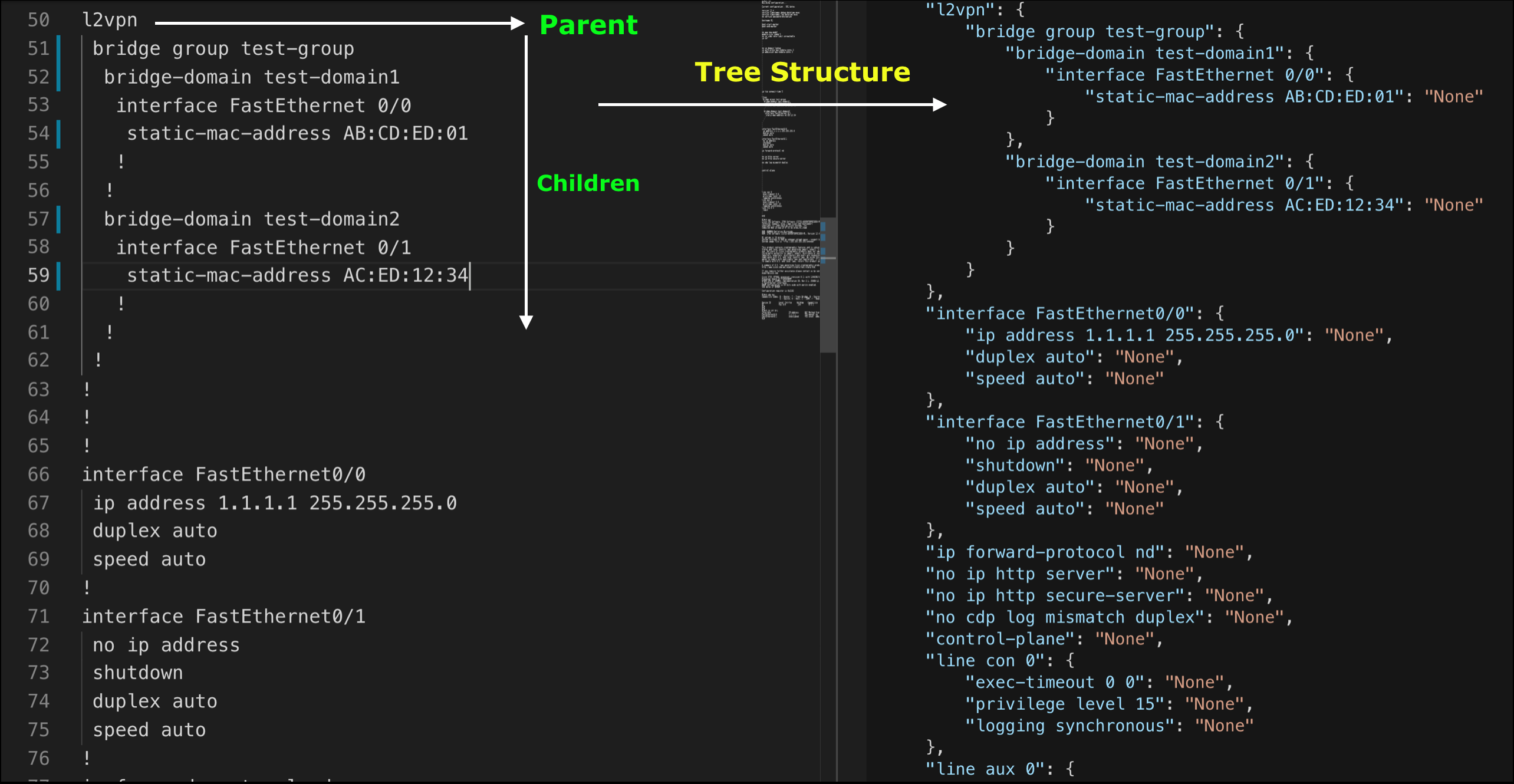
- Tree structure
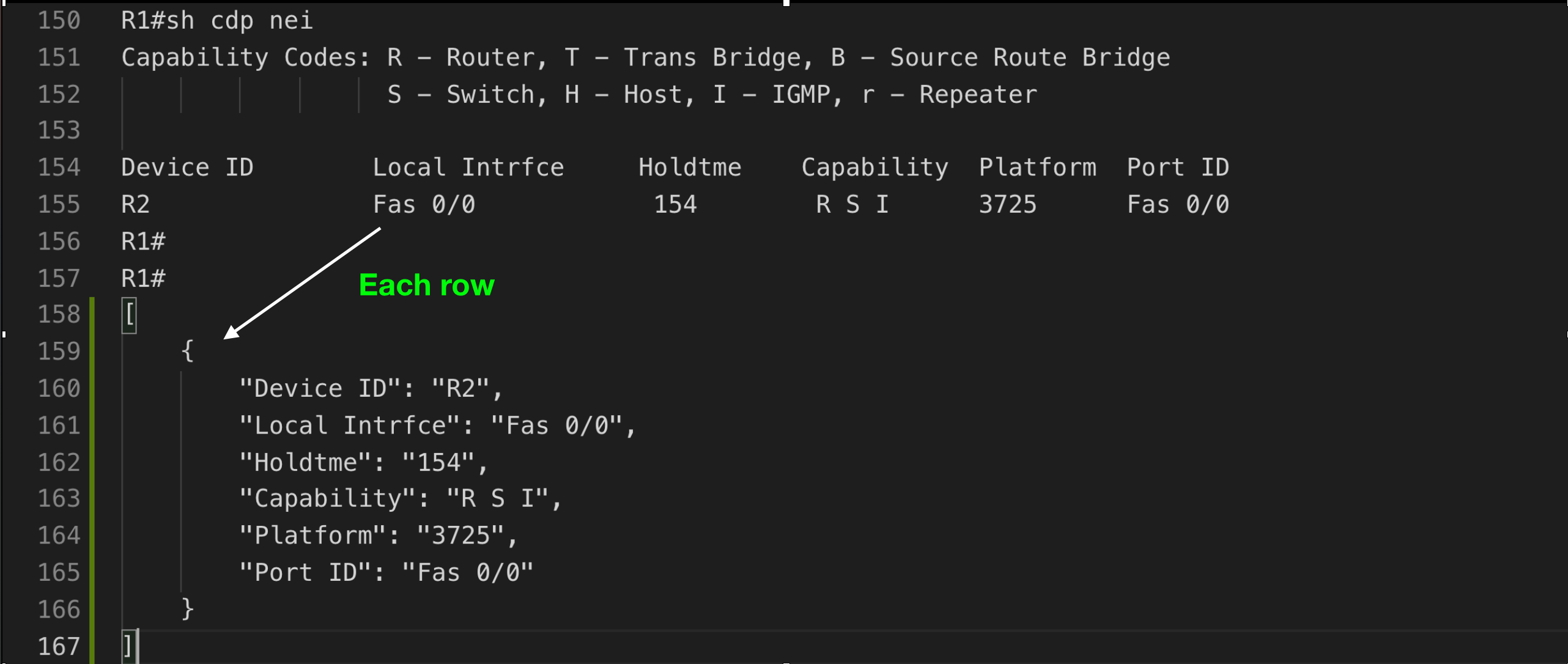
i.e. show running - Table structure
i.e. show ip interface - Data
i.e. show version
Tree Structure
Table Structure
✨ Zero Dependencies - Uses only Python standard library
⚡ Fast - Modern tooling with uv package manager support
🔒 Type Safe - Full type hints and py.typed marker
🎯 Vendor Independent - Works with any network device configuration
📊 Multiple Formats - Parse trees, tables, and unstructured data
🧪 Well Tested - 80%+ code coverage, tested on Python 3.8-3.13
pip install shconfparserFaster with uv:
curl -LsSf https://astral.sh/uv/install.sh | sh
uv pip install shconfparserSingle show command:
from shconfparser.parser import Parser
p = Parser()
data = p.read('running_config.txt')
# Parse directly (no split needed for single show running command)
tree = p.parse_tree(data)
print(p.dump(tree, indent=2))Alternative: Access internal properties
p = Parser()
p.read('running_config.txt')
# Access reader data directly
tree = p.parse_tree(p.r.data)
print(p.dump(tree, indent=4))Multiple show commands in one file:
from shconfparser.parser import Parser
p = Parser()
data = p.read('multiple_commands.txt') # Contains multiple show outputs
data = p.split(data) # Split into separate commands
data.keys()
# odict_keys(['running', 'version', 'cdp_neighbors', 'ip_interface_brief'])
# Now parse each command separately
data['running'] = p.parse_tree(data['running'])
headers = ['Device ID', 'Local Intrfce', 'Holdtme', 'Capability', 'Platform', 'Port ID']
data['cdp_neighbors'] = p.parse_table(data['cdp_neighbors'], header_names=headers)
print(p.dump(data['running'], indent=2))Alternative: Access internal properties
p = Parser()
p.read('multiple_commands.txt')
p.split(p.r.data)
# Access split data from internal property
data = p.s.shcmd_dict
data['running'] = p.parse_tree(data['running'])
print(p.dump(data['running'], indent=4))import shconfparser
print(shconfparser.__version__) # '3.0.0'from shconfparser.parser import Parser
p = Parser()
# Single command file - parse directly
data = p.read('running_config.txt')
tree = p.parse_tree(data) # No split() needed
# Access nested configuration
print(p.dump(tree['interface FastEthernet0/0'], indent=2))
# {
# "ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.0": null,
# "duplex auto": null,
# "speed auto": null
# }# Single command file
p = Parser()
data = p.read('cdp_neighbors.txt')
# Parse table directly (no split needed)
headers = ['Device ID', 'Local Intrfce', 'Holdtme', 'Capability', 'Platform', 'Port ID']
cdp_data = p.parse_table(data, header_names=headers)
# Access as list of dictionaries
for neighbor in cdp_data:
print(f"{neighbor['Device ID']} on {neighbor['Local Intrfce']}")
# Output: R2 on Fas 0/0# Single command file
p = Parser()
data = p.read('show_version.txt')
# Parse show version output directly
version_data = p.parse_data(data) # No split() needed
# Search for specific information
import re
for line in version_data.keys():
if re.search(r'IOS.*Version', line):
print(line)
# Output: Cisco IOS Software, 3700 Software (C3725-ADVENTERPRISEK9-M), Version 12.4(25d)...# Search for all interfaces
pattern = r'interface\s+\w+.*'
matches = p.search.search_all_in_tree(pattern, tree)
for key, value in matches.items():
print(value)
# interface FastEthernet0/0
# interface FastEthernet0/1# Find specific device in CDP table
pattern = r'R\d+'
match = p.search.search_in_table(pattern, cdp_data, 'Device ID')
print(match)
# {'Device ID': 'R2', 'Local Intrfce': 'Fas 0/0', ...}For advanced users who need granular control
from shconfparser import Reader, ShowSplit, TreeParser, TableParser
# For multiple show commands
reader = Reader('multiple_commands.txt')
splitter = ShowSplit()
data = splitter.split(reader.data) # Split only if multiple commands
# Use specific parsers
tree_parser = TreeParser()
table_parser = TableParser()
running = tree_parser.parse(data['running'])
cdp = table_parser.parse(data['cdp_neighbors'], header_names=headers)💡 Remember: Use split() only when your file contains multiple show commands. For single command files, parse directly.
📖 For more examples, see docs/ folder.
📚 Complete documentation: docs/README.md
| Guide | Description |
|---|---|
| Usage Examples | Detailed parsing examples (tree, table, data) |
| API Reference | Complete API documentation |
| Migration Guide | Upgrade from v2.x to v3.0 |
| Python Compatibility | Python version support |
| Guide | Description |
|---|---|
| Quick Start | 5-minute contributor setup |
| Contributing Guide | How to contribute |
| Architecture | System design and structure |
| Business Standards | Quality and compliance standards |
- 📖 Documentation: docs/README.md
- 🐛 Bug Reports: GitHub Issues
- 💬 Questions: Stack Overflow (tag:
shconfparser) - 📧 Email: kirankotari@live.com
Q: What Python versions are supported?
A: Python 3.8-3.13 are fully tested and supported.
Q: Does this work with my network vendor?
A: Yes! shconfparser is vendor-independent and works with any hierarchical configuration format.
Q: Are there any dependencies?
A: No runtime dependencies - uses only Python standard library.
Q: How do I migrate from v2.x?
A: The API is backward compatible. Just run pip install --upgrade shconfparser. See Migration Guide for details.
- 🌟 Star us on GitHub
- 🤝 Contribute: See CONTRIBUTING.md
- 📊 CI/CD: Automated testing on Python 3.8-3.13 across Ubuntu, macOS, Windows
MIT License © 2016-2025 Kiran Kumar Kotari
Special thanks to all contributors