-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 0
github tutorial Youtube
Youtube Video:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=RGOj5yH7evk
git / version control = way to track code changes
repo = folder where the project is kept
git = tool that tracks the changes over time
githib = website where we keep all our repo
- clone -> bring a repo hosted somewhere (for instance on github) into a folder on your local machine
- add -> track your files and changes in git
- commit -> save your files in git
- push -> upload git to a remote repo (like github)
- pull -> download changes from remote repo to local machine
repo = project that contains all my files for a specific project
To create new repo:
Select: README, LICENSE, and .gitignore
(It is recommended that every repository include a README, LICENSE, and .gitignore)
This is a file that describe what the project is about.
You can create the README.md file directly on github or you can create it locally.
create a new repository on the command line
echo "# demo-repo2" >> README.md
git init
git add README.md
git commit -m "first commit"
git branch -M main
git remote add origin https://github.com/cecilehannay/demo-repo2.git
git push -u origin main
push an existing repository from the command line
git remote add origin https://github.com/cecilehannay/demo-repo2.git
git branch -M main
git push -u origin main
git clone git@github.com:cecilehannay/github-tutorial.git
cd github-tutorial
The directory github-tutorial contains a file .git that contains all the changes recorded in the history of the repo.
Edit README.md
git status
shows the files that haven't been saved yet in the local repo (it can be files that have been modified
modified:
or files that haven't been saved in the repo)
Untracked files:
git add .
stage the files with git and they are ready to be committed.
git commit -m "Modified the README.md on local repo" -m "Description of the change "
Now the changes is on the local repo
Check what the origin is:
git remote -v
returns
origin git@github.com:cecilehannay/github-tutorial.git (fetch)
origin git@github.com:cecilehannay/github-tutorial.git (push)
git push origin master Origin = the location of our git repo Master = the branch we want to push to
TO avoid to add each time "origin master"
Enter the first time
git push -u origin master
and after
git push
To make a directory a git
 )
)
We are on the main branch. This is the default branch on the repo. If only one branch, this will be the branch
 )
)
If we are have several branches, it starts looking like a tree:
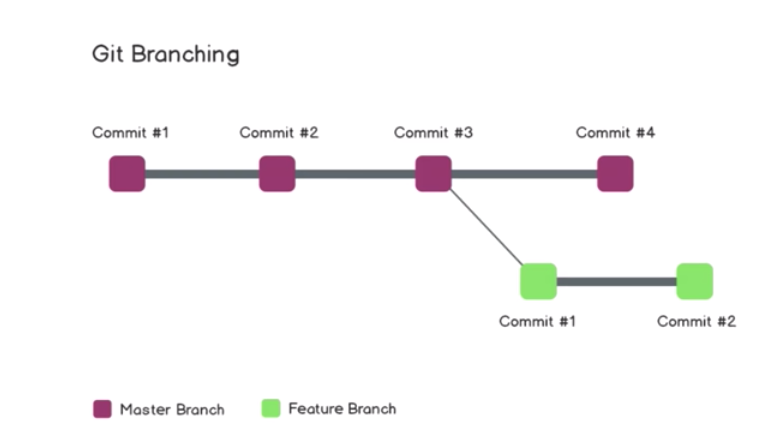
Let's say we want to create a new branch called "feature branch" At first the code will be exactly the same on the main branch and the feature branch. But as we make changes on the feature branch, The other branch don't see each other. We want to have a feature branch to make our changes before bringing them back to the main branch.
Very useful, for instance, if we have a bug on the main branch.
We create another branch called the "hot fix branch"
 )
)
Let's do an example:
I am a repo called demo-repo on gitub. I clone it locally
git clone git@github.com:cecilehannay/demo-repo.git
If I type:
git branch
It will return
- main
I show I only have one branch and the * shows that I am on that branch.
To create a new branch
git checkout -b feature-readme-instructions
where feature-readme-instructions **is the name of the branch -b means I am creating a new brancj
Switched to a new branch 'feature-readme-instructions'
Use git checkout to switch between branches main
git checkout main
git checkout feature-readme-instructions
git diff feature-readme-instructions main
push on the branch
git push
If you get the error:
You didn't specify any refspecs to push, and push.default is "nothing".
Try to use (-u is the same as --set-upstream)
git push --set-upstream origin feature-readme-instructions
git push -u origin feature-readme-instructions
This gives a hint on how to create a pull request on github by giving the instructions
A pull request is a request to have your code pulled into another branch,
In our case we want to do a PR from the feature branch to the master branch
Once the PR is merged, you generally delete your feature branch and switch to master branch.
To merge PR go to github
After doing the merge on github, go back to the branch
git checkout main
git branch
git pull origin main
Delete the branch
git branch -d feature-readme-instructions
Often it is harder because there will be conflicts
Say I have done changes on the same line of README.md in the main branch and quick-test branch
Let's say I work on a branch called quick-test. I want to regularly merge the main branch with my quick-test branch to make sure I don't fall behind.
git merge main
But if I had conflict I will get the message
error: Merging is not possible because you have unmerged files.
hint: Fix them up in the work tree, and then use 'git add/rm '
hint: as appropriate to mark resolution and make a commit.
fatal: Exiting because of an unresolved conflict.
Edit the file which there is conflict to resolve the conflict markers.
git status
git diff
git add README.md
git commit -am "update my current branch with the main branch "
Generate a key locally
ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 4096 -C "hannay@ucar.edu"
+> this generates 2 keys private and public